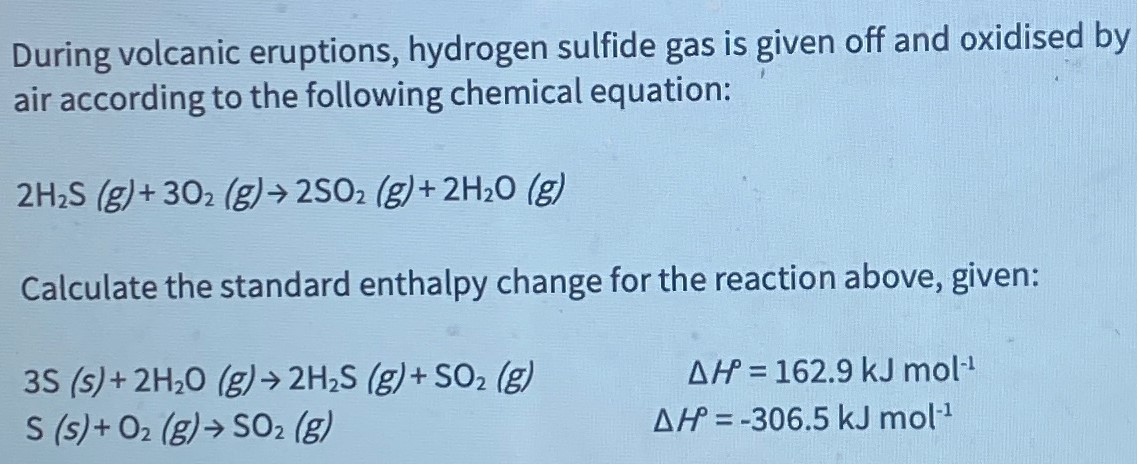During volcanic eruptions, hydrogen sulfide gas is given off and oxidised by air according to the following chemical equation: 2 H2S(g) + 3O2(g) → 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(g) Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction above, given: 3S(s) + 2H2O(g) → 2H2S(g) + SO2(g) ΔHP = 162.9 kJ mol−1 S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) ΔH = −306.5 kJ mol−1