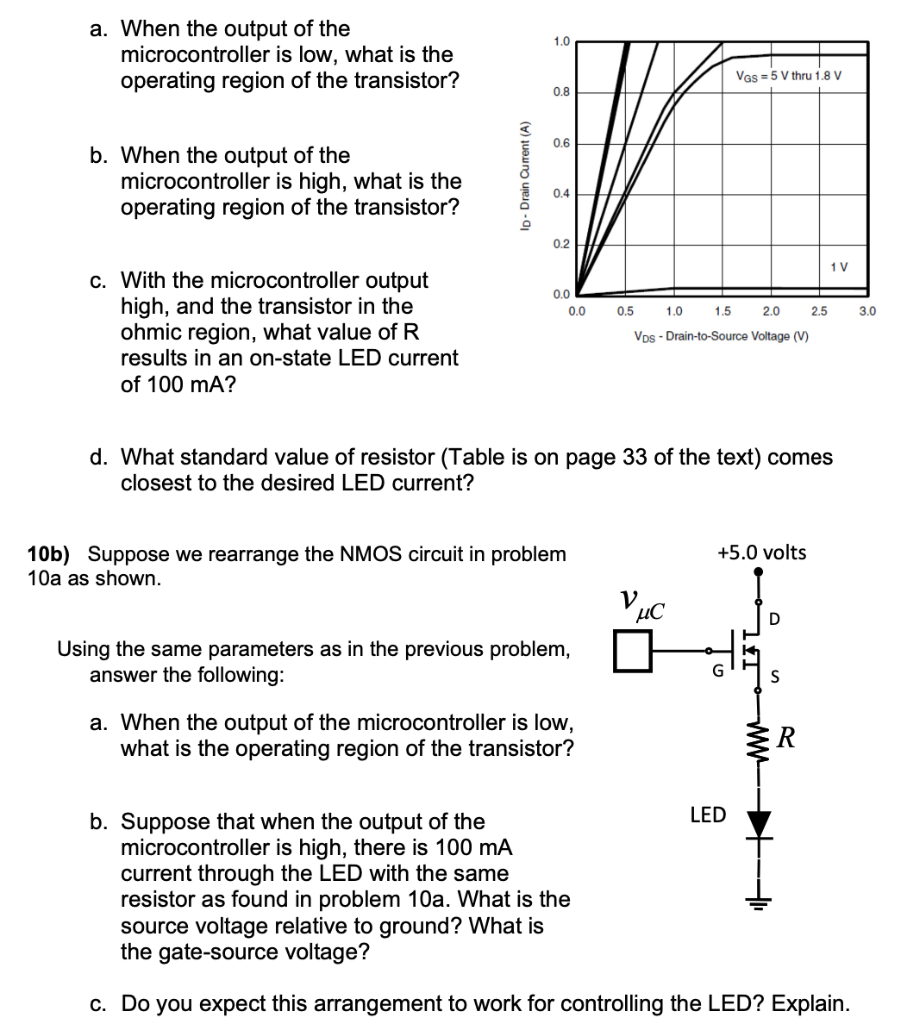
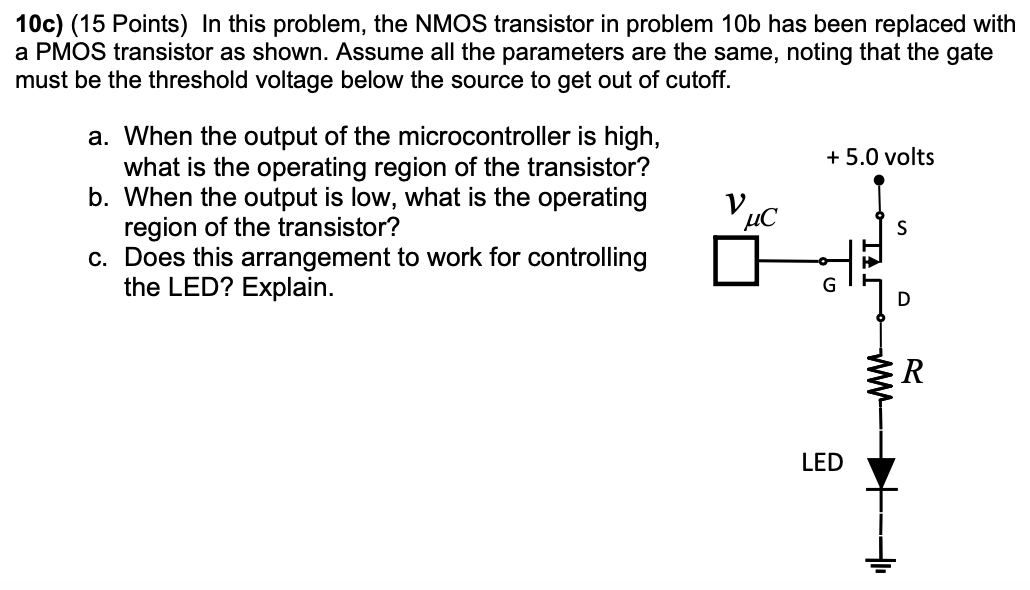
10a) (15 Points) In the following circuit, an NMOS transistor is used to switch the current to the LED. Assume the following parameters: Microcontroller: vO = 4.6 V iOH < −5 mA and vOL = 0.4 V, iOL < 8 mA LED: vf = 2.0 V, PLED−max = 200 mW Desired LED current 100 mA Transistor: vT = 1.0 V, RDS(ON) = 0.5 Ω, iD−max = 500 mA a. When the output of the microcontroller is low, what is the operating region of the transistor? b. When the output of the microcontroller is high, what is the operating region of the transistor? c. With the microcontroller output high, and the transistor in the ohmic region, what value of R results in an on-state LED current of 100 mA? d. What standard value of resistor (Table is on page 33 of the text) comes closest to the desired LED current? 10b) Suppose we rearrange the NMOS circuit in problem 10 as shown. Using the same parameters as in the previous problem, answer the following: a. When the output of the microcontroller is low, what is the operating region of the transistor? b. Suppose that when the output of the microcontroller is high, there is 100 mA current through the LED with the same resistor as found in problem 10a. What is the source voltage relative to ground? What is the gate-source voltage? c. Do you expect this arrangement to work for controlling the LED? Explain. 10c) (15 Points) In this problem, the NMOS transistor in problem 10b has been replaced with a PMOS transistor as shown. Assume all the parameters are the same, noting that the gate must be the threshold voltage below the source to get out of cutoff. a. When the output of the microcontroller is high, what is the operating region of the transistor? b. When the output is low, what is the operating region of the transistor? c. Does this arrangement to work for controlling the LED? Explain.