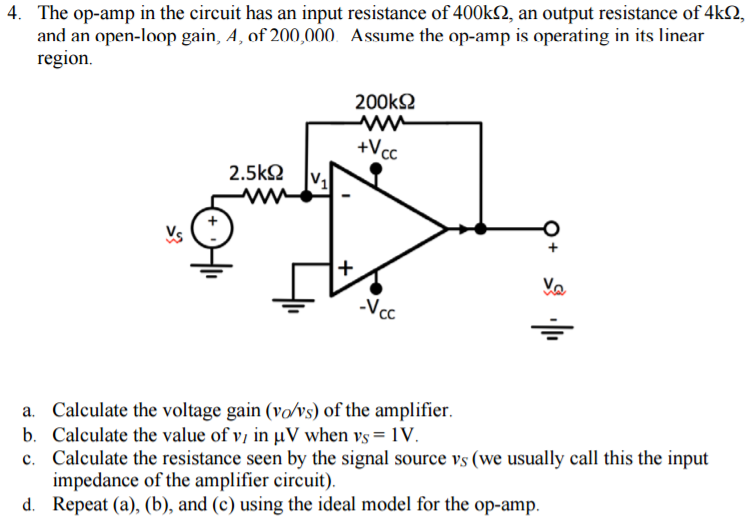
4. The op-amp in the circuit has an input resistance of 400kΩ, an output resistance of 4kΩ, and an open-loop gain, A, of 200,000. Assume the opamp is operating in its linear region. a. Calculate the voltage gain (vO/vS) of the amplifier. b. Calculate the value of vl in µV when vS = 1 V. c. Calculate the resistance seen by the signal source vS (we usually call this the input impedance of the amplifier circuit). d. Repeat (a), (b), and (c) using the ideal model for the op-amp.


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers