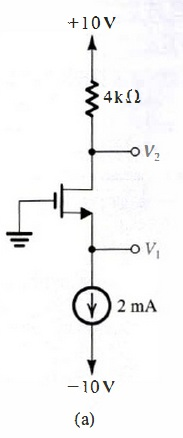
5.106 For the circuit in Fig. 5.55 (a) with I = 0.2 mA, RG = 0, RD = 10 kΩ, and VDD = 2.5 V, consider the behavior in each of the following two cases. In each case, find the voltages VS, VD, and VDS that result. (a) Vt = 1 V and kn = 1.6 mA/v2 (b) Vt = 0.8 V and kn = 1.25 mA/V2