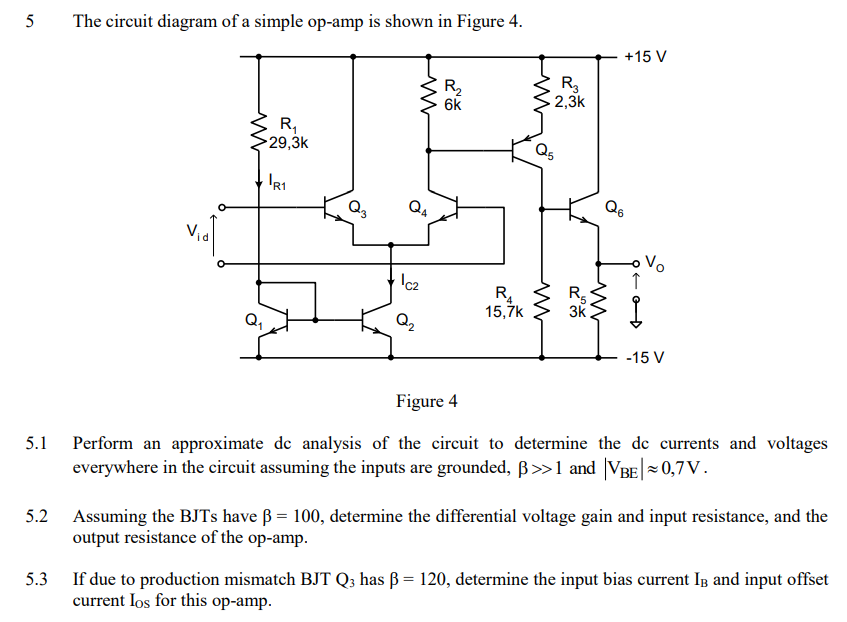
5 The circuit diagram of a simple op-amp is shown in Figure 4. Figure 4 5.1 Perform an approximate dc analysis of the circuit to determine the dc currents and voltages everywhere in the circuit assuming the inputs are grounded, β > 1 and |VBE| ≈ 0,7 V. 5.2 Assuming the BJTs have β = 100, determine the differential voltage gain and input resistance, and the output resistance of the op-amp. 5.3 If due to production mismatch BJTQ has β = 120, determine the input bias current IB and input offset current IOS for this op-amp.