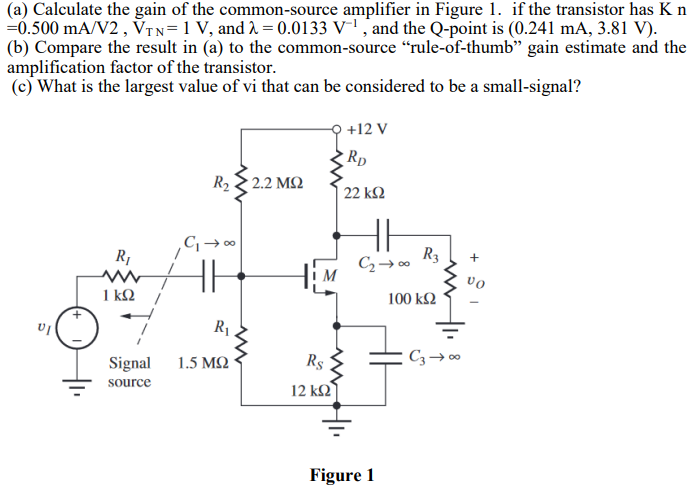
(a) Calculate the gain of the common-source amplifier in Figure 1. if the transistor has Kn = 0.500 mA/V2, VTN = 1 V, and λ = 0.0133 V−1, and the Q-point is (0.241 mA, 3.81 V). (b) Compare the result in (a) to the common-source "rule-of-thumb" gain estimate and the amplification factor of the transistor. (c) What is the largest value of vi that can be considered to be a small-signal? Figure 1