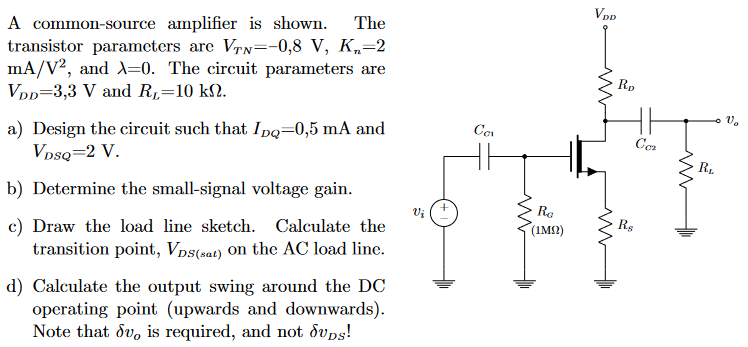
A common-source amplifier is shown. The transistor parameters are VTN = −0,8 V, Kn = 2 mA/V2, and λ = 0. The circuit parameters are VDD = 3,3 V and RL = 10 kΩ. a) Design the circuit such that IDQ = 0,5 mA and VDSQ = 2 V. b) Determine the small-signal voltage gain. c) Draw the load line sketch. Calculate the transition point, VDS(sat) on the AC load line. d) Calculate the output swing around the DC operating point (upwards and downwards). Note that δvo is required, and not δvDS!