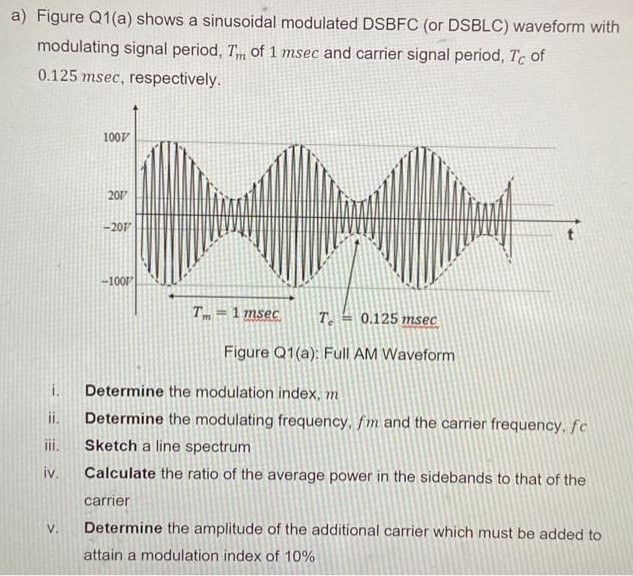
a) Figure Q1(a) shows a sinusoidal modulated DSBFC (or DSBLC) waveform with modulating signal period, Tm of 1 msec and carrier signal period, TC of 0.125 msec, respectively. Figure Q1 (a): Full AM Waveform i. Determine the modulation index, m ii. Determine the modulating frequency, fm and the carrier frequency, fc iii. Sketch a line spectrum iv. Calculate the ratio of the average power in the sidebands to that of the carrier v. Determine the amplitude of the additional carrier which must be added to attain a modulation index of 10%