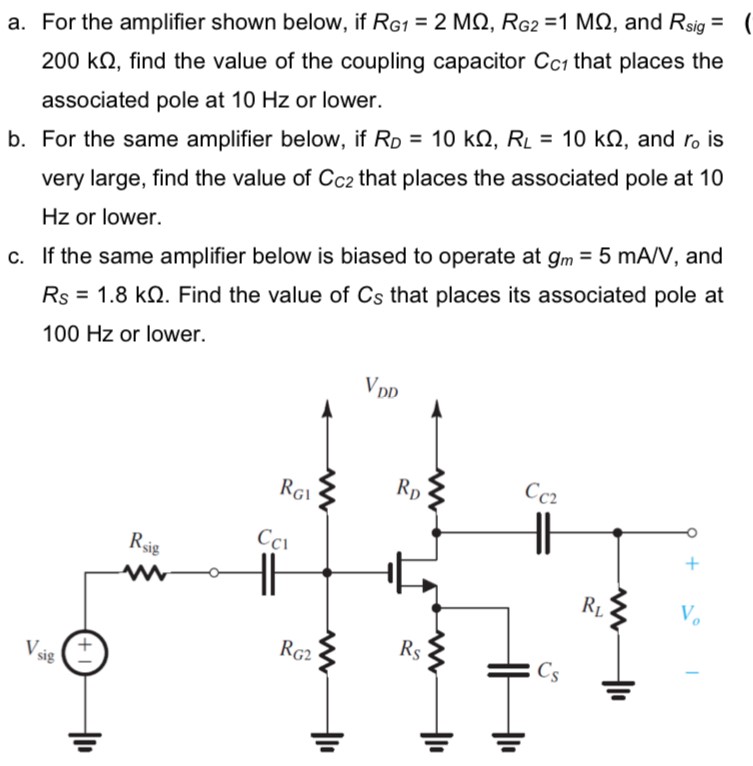
a. For the amplifier shown below, if RG1 = 2 MΩ, RG2 = 1 MΩ, and Rsig = 200 kΩ, find the value of the coupling capacitor CC1 that places the associated pole at 10 Hz or lower. b. For the same amplifier below, if RD = 10 kΩ, RL = 10 kΩ, and r0 is very large, find the value of CC2 that places the associated pole at 10 Hz or lower. c. If the same amplifier below is biased to operate at gm = 5 mA/V, and RS = 1.8 kΩ. Find the value of CS that places its associated pole at 100 Hz or lower.