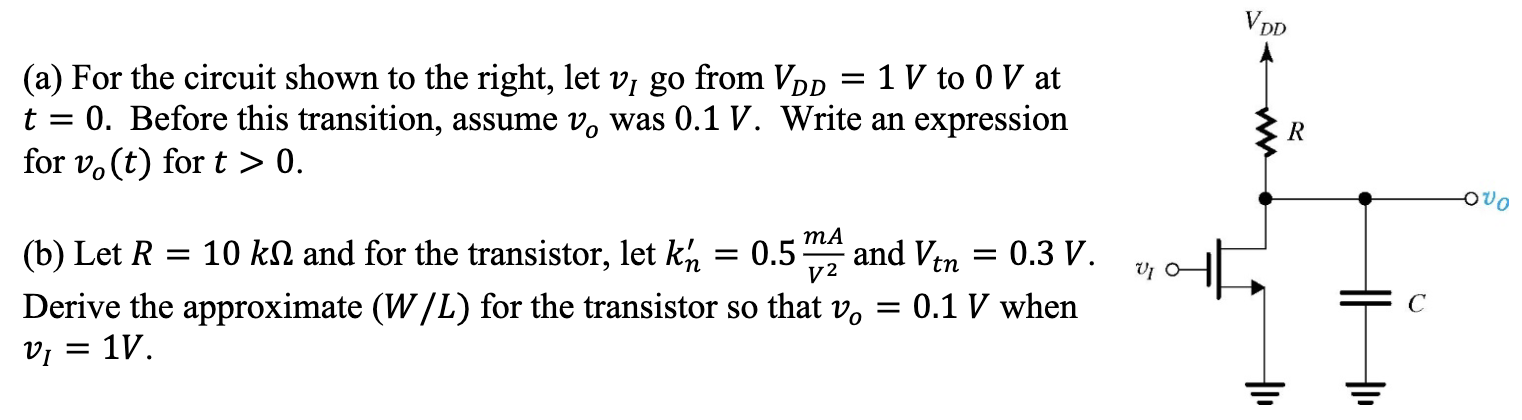(a) For the circuit shown to the right, let vI go from VDD = 1 V to 0 V at t = 0. Before this transition, assume vo was 0.1 V. Write an expression for vo(t) for t > 0. (b) Let R = 10 kΩ and for the transistor, let kn′ = 0.5 mA/V2 and Vtn = 0.3 V. Derive the approximate (W/L) for the transistor so that vo = 0.1 V when vI = 1 V