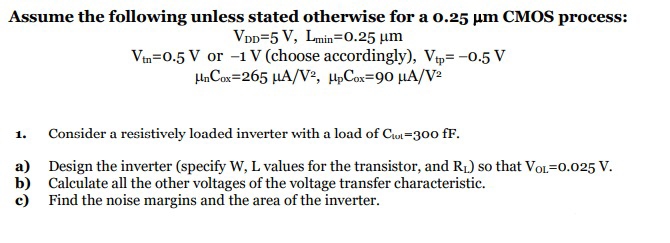
Assume the following unless stated otherwise for a 0.25 μm CMOS process: VDD = 5 V, Lmin = 0.25 μm Vtn = 0.5 V or −1 V (choose accordingly), Vtp = −0.5 V μnCox = 265 μA/V2, μpCox = 90 μA/V2 Consider a resistively loaded inverter with a load of Ctot = 300 fF. a) Design the inverter (specify W, L values for the transistor, and RL) so that VOL = 0.025 V. b) Calculate all the other voltages of the voltage transfer characteristic. c) Find the noise margins and the area of the inverter.