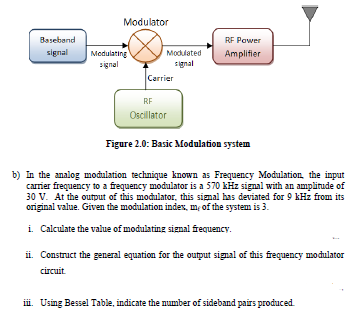
b) In the analog modulation technique known as Frequency Modulation, the input carrier frequency to a frequency modulator is a 570 kHz signal with an amplitude of 30 V. At the output of this modulator, this signal has deviated for 9 kHz from its original value. Given the modulation index, mf of the system is 3. i. Calculate the value of modulating signal frequency. ii. Construct the general equation for the output signal of this frequency modulator circuit. iii. Using Bessel Table, indicate the number of sideband pairs produced. Figure 2.0: Basic Modulation system