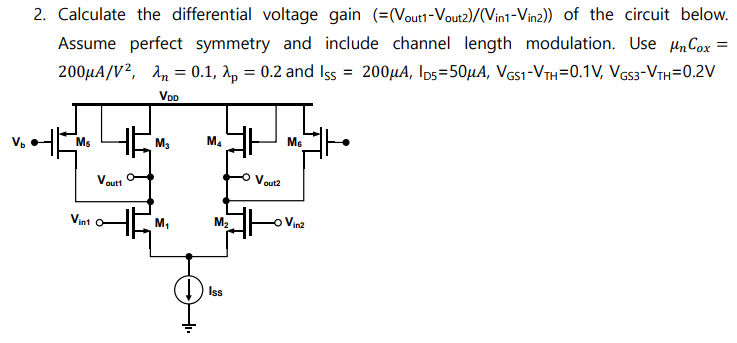
Calculate the differential voltage gain ( =(Vout1 − Vout2)/(Vin1 − Vin2)) of the circuit below. Assume perfect symmetry and include channel length modulation. Use μnCox = 200 μA/V2, λn = 0.1, λp = 0.2 and ISS = 200 μA, ID5 = 50 μA, VGS−VTH = 0.1 V, VGS3−VTH = 0.2 V


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers