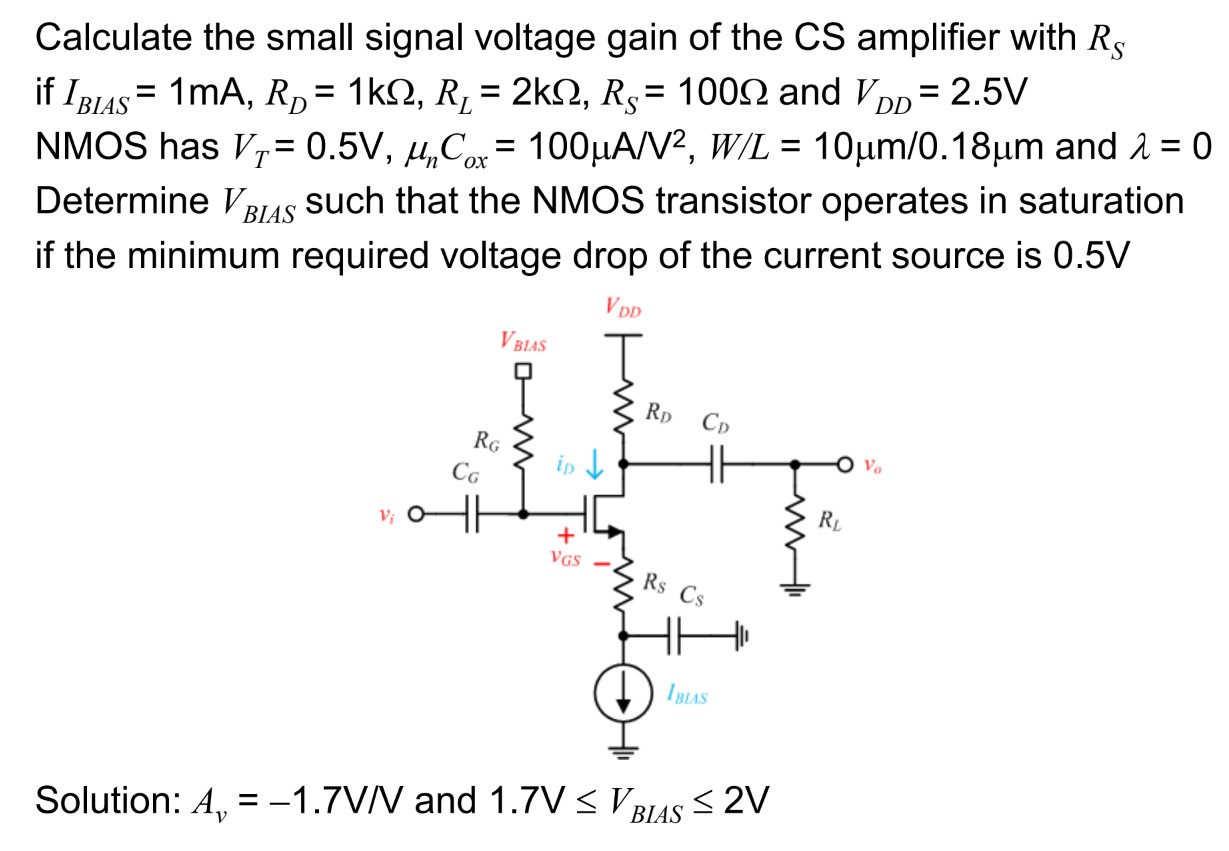
Calculate the small signal voltage gain of the CS amplifier with RS if IBIAS = 1 mA, RD = 1 kΩ, RL = 2 kΩ, RS = 100 Ω and VDD = 2.5 V NMOS has VT = 0.5 V, μnCox = 100 μA/V2, W/L = 10 μm/0.18 μm and λ = 0 Determine VBIAS such that the NMOS transistor operates in saturation if the minimum required voltage drop of the current source is 0.5 V Solution: Av = −1.7 V/V and 1.7 V ≤ VBIAS ≤ 2 V