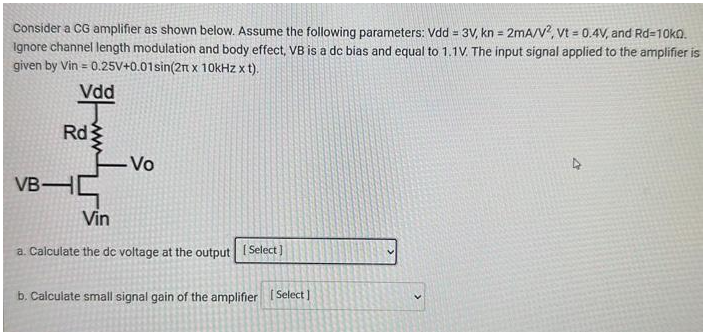
Consider a CG amplifier as shown below. Assume the following parameters: Vdd = 3V, kn = 2mA/V^2, Vt = 0.4V, and Rd = 10 kohm. Ignore channel length modulation and body effect, VB is a dc bias and equal to 1.1V. The input signal applied to the amplifier is given by Vin = 0.25V+0.01sin(2pi x 10kHz x t). a. Calculate the de voltage at the output b. Calculate small signal gain of the amplifier


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers