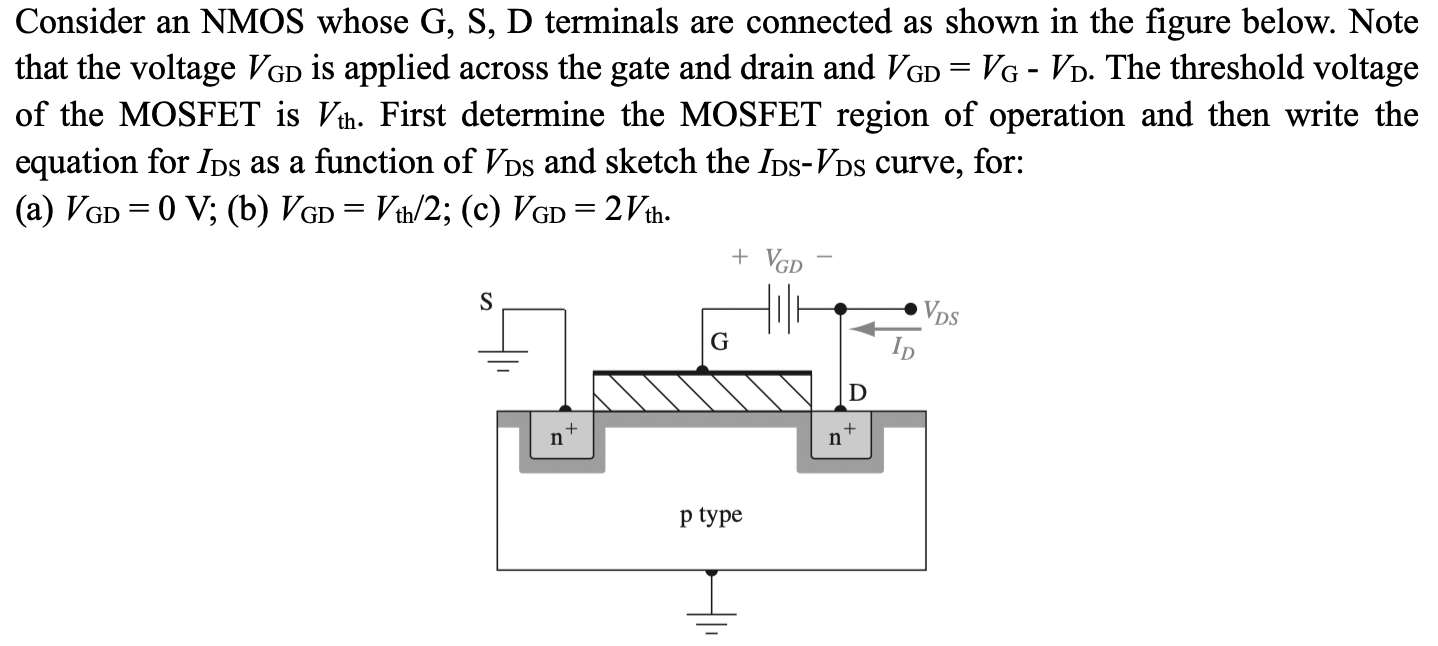
Consider an NMOS whose G, S, D terminals are connected as shown in the figure below. Note that the voltage VGD is applied across the gate and drain and VGD = VG−VD. The threshold voltage of the MOSFET is Vth . First determine the MOSFET region of operation and then write the equation for IDS as a function of VDS and sketch the IDS−VDS curve, for: (a) VGD = 0 V; (b) VGD = Vth/2; (c) VGD = 2 Vth.