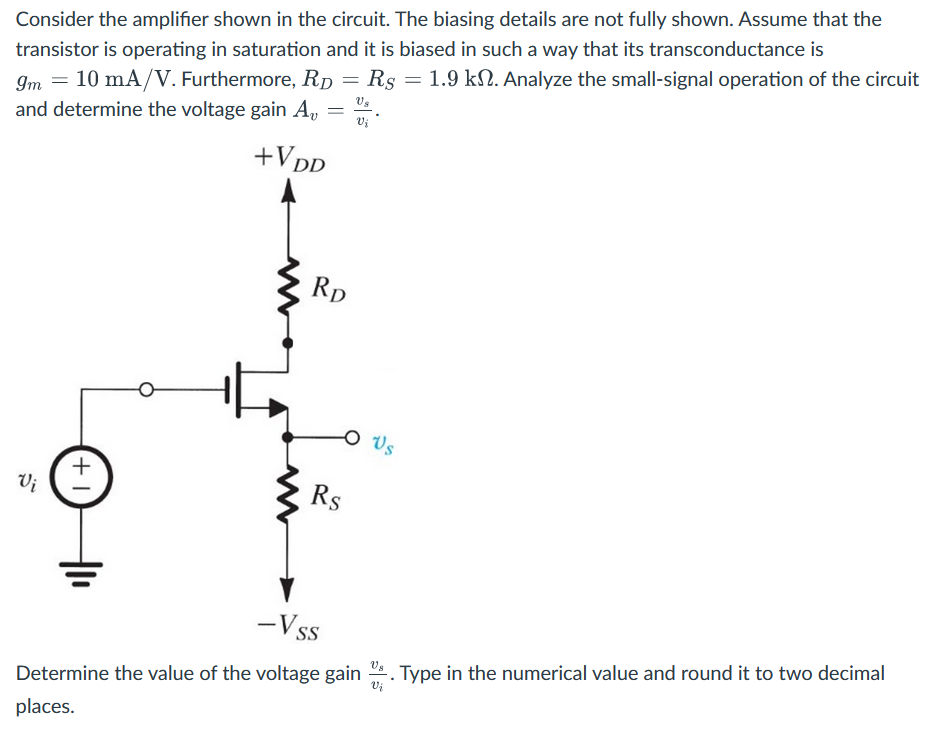
Consider the amplifier shown in the circuit. The biasing details are not fully shown. Assume that the transistor is operating in saturation and it is biased in such a way that its transconductance is gm = 10 mA/V. Furthermore, RD = RS = 1.9 kΩ. Analyze the small-signal operation of the circuit and determine the voltage gain Av = vs/vi. Determine the value of the voltage gain vs/vi. Type in the numerical value and round it to two decimal places.