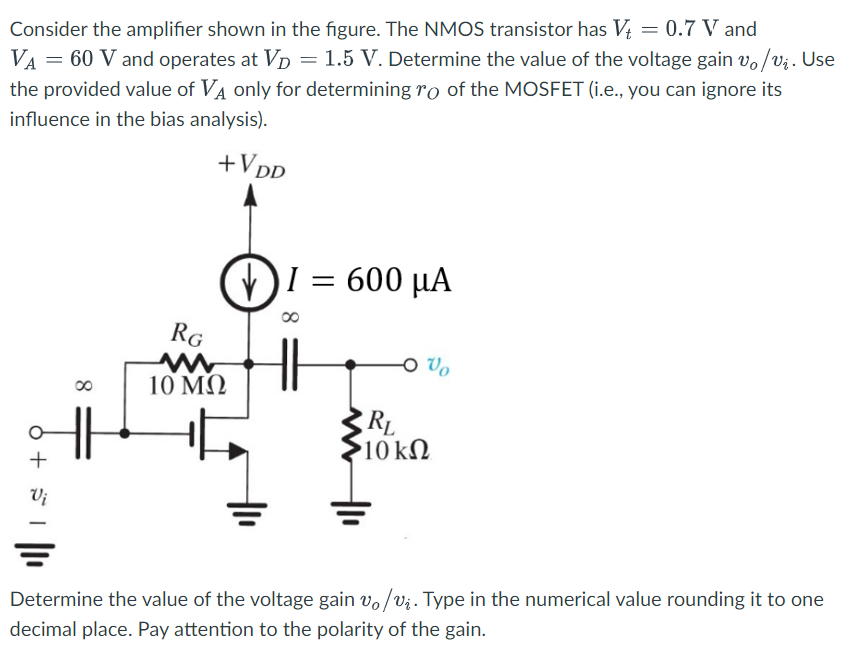
Consider the amplifier shown in the figure. The NMOS transistor has Vt = 0.7 V and VA = 60 V and operates at VD = 1.5 V. Determine the value of the voltage gain vo/vi. Use the provided value of VA only for determining rO of the MOSFET (i. e. , you can ignore its influence in the bias analysis). Determine the value of the voltage gain vo/vi. Type in the numerical value rounding it to one decimal place. Pay attention to the polarity of the gain.