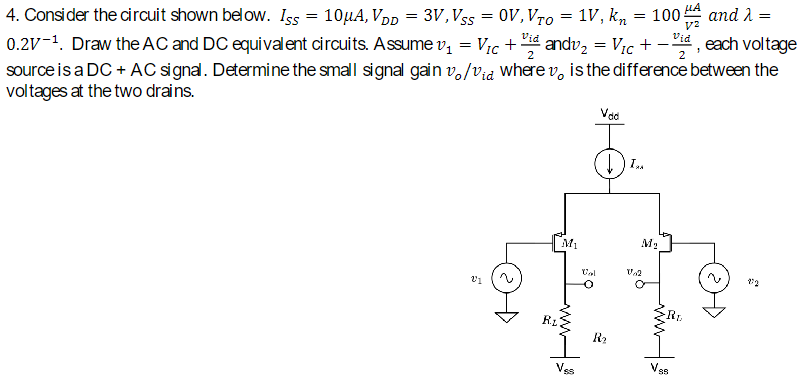
Consider the circuit shown below. ISS = 10 μA, VDD = 3 V, VSS = 0 V, VTO = 1 V, kn = 100 μA V2 and λ = 0.2 V−1. Draw the AC and DC equivalent circuits. Assume v1 = VIC + vid 2 and v2 = VIC + −vid 2, each voltage source is a DC + AC signal. Determine the small signal gain vo/vid where vo is the difference between the voltages at the two drains.