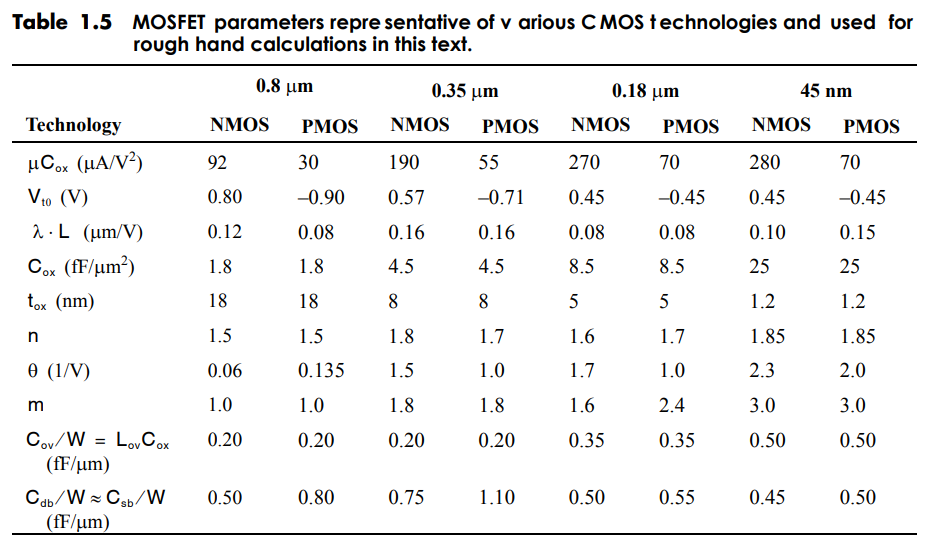
Consider the common-source amplifier shown in Fig. P3.11. The transistors are sized (W/L)1 = 6 µm/0.3 µm and (W/L)2 = 4 µm/0.3 µm. Transistor Q1 is biased so that Veff1 = 200 mV. Using the 0.18−µm CMOS device parameters in Table 1.5, and assuming a supply voltage of 1.8 V, estimate: a. the power consumption of the amplifier b. the small-signal output resistance of the amplifier c. the small-signal gain of the amplifier, vout /vin



You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers