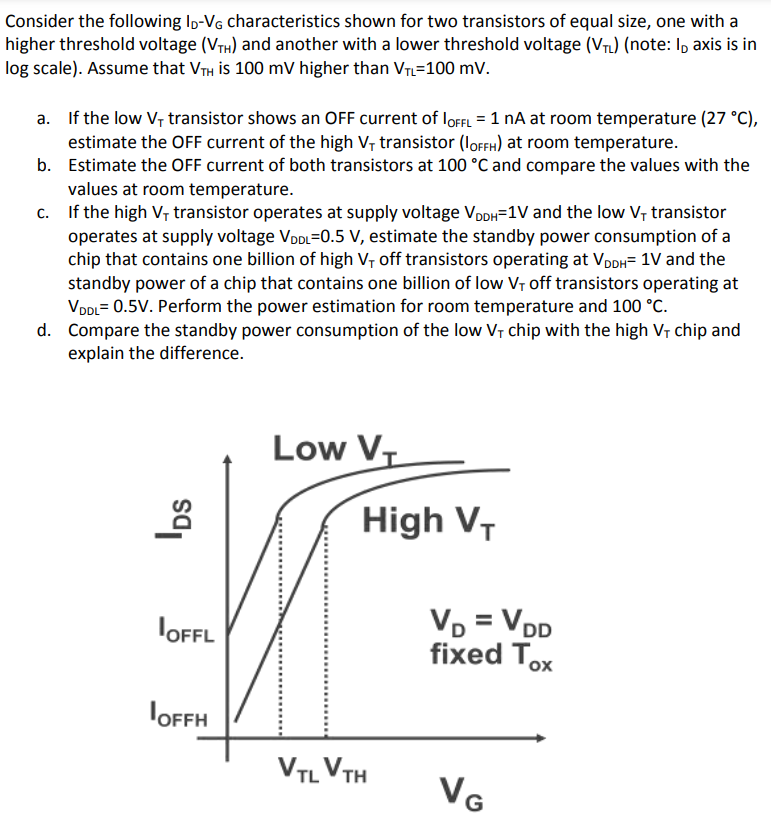
Consider the following ID−VG characteristics shown for two transistors of equal size, one with a higher threshold voltage (VTH) and another with a lower threshold voltage (VTL) (note: ID axis is in log scale). Assume that VTH is 100mV higher than VTL = 100 mV. a. If the low VT transistor shows an OFF current of IOFFL = 1 nA at room temperature (27∘C), estimate the OFF current of the high VT transistor (IOFFH) at room temperature. b. Estimate the OFF current of both transistors at 100∘C and compare the values with the values at room temperature. c. If the high VT transistor operates at supply voltage VDDH = 1 V and the low VT transistor operates at supply voltage VDDL = 0.5 V, estimate the standby power consumption of a chip that contains one billion of high VT off transistors operating at VDDH = 1 V and the standby power of a chip that contains one billion of low VT off transistors operating at VDDL = 0.5 V. Perform the power estimation for room temperature and 100∘C. d. Compare the standby power consumption of the low VT chip with the high VT chip and explain the difference.