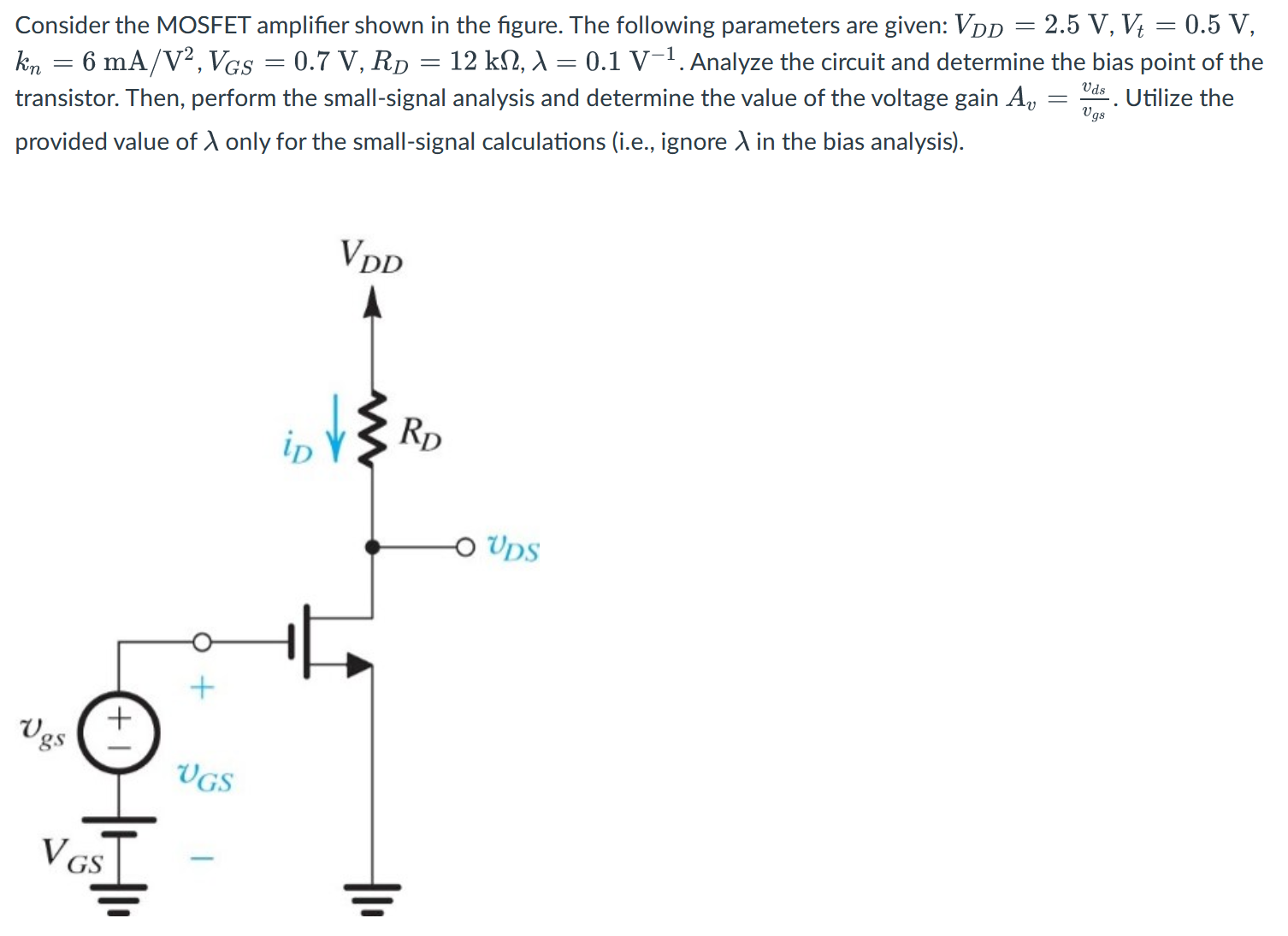
Consider the MOSFET amplifier shown in the figure. The following parameters are given: VDD = 2.5 V, Vt = 0.5 V, kn = 6 mA/V2, VGS = 0.7 V, RD = 12 kΩ, λ = 0.1 V−1. Analyze the circuit and determine the bias point of the transistor. Then, perform the small-signal analysis and determine the value of the voltage gain Av = vds/vgs. Utilize the provided value of λ only for the small-signal calculations (i.e., ignore λ in the bias analysis).