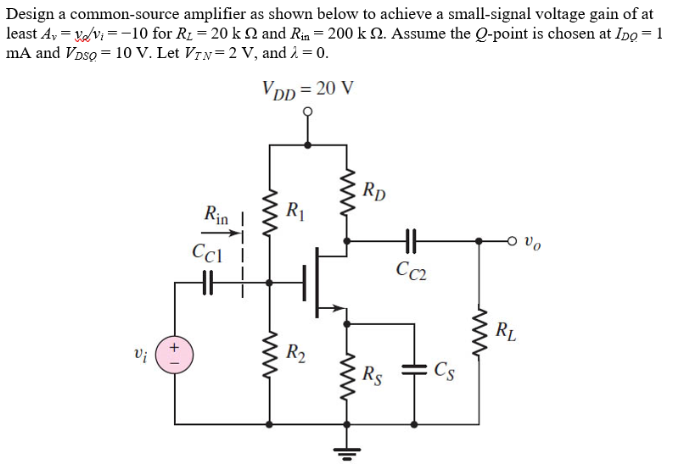
D4.29 Design a common-source amplifier, such as that in Figure P4.29, to achieve a small-signal voltage gain of at least Av = vo/vi = -10 for RL = 20 kohm and Rin = 200 kohm. Assume the Q-point is chosen at IDQ = 1 mA and VDSQ = 10 V. Let VT N = 2 V, and λ = 0. Design a common-source amplifier as shown below to achieve a small-signal voltage gain of at least Av = vo/vi = -10 for RL = 20 kohm and Rin = 200 kohm. Assume the Q-point is chosen at IDQ = 1 mA and VDSQ = 10 V. Let VT N = 2 V, and λ = 0.


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers