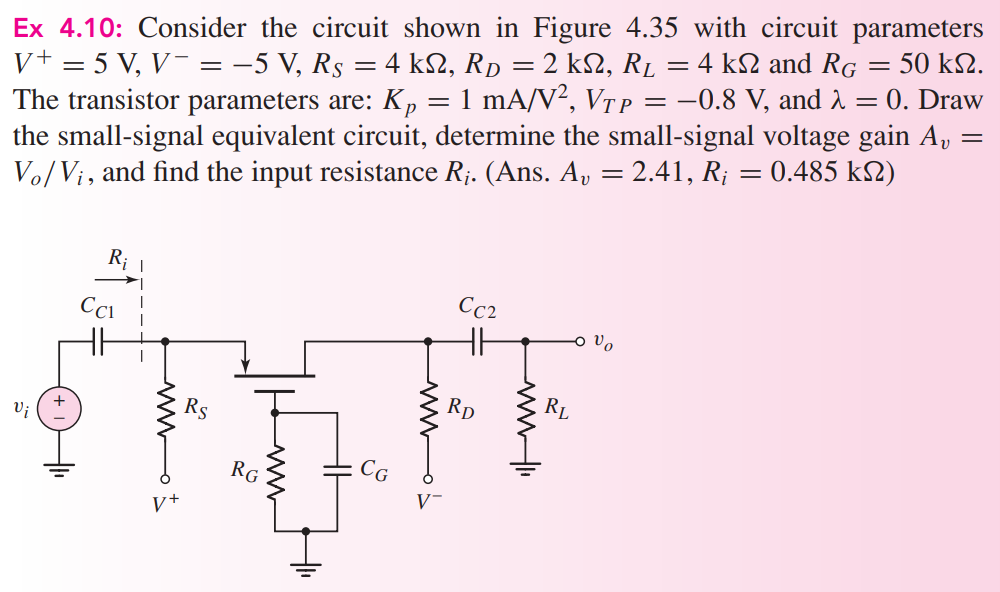
Ex 4.10: Consider the circuit shown in Figure 4.35 with circuit parameters V+ = 5 V, V− = −5 V, RS = 4 kΩ, RD = 2 kΩ, RL = 4 kΩ and RG = 50 kΩ. The transistor parameters are: Kp = 1 mA/V2, VTP = −0.8 V, and λ = 0. Draw the small-signal equivalent circuit, determine the small-signal voltage gain Av = Vo/Vi, and find the input resistance Ri. (Ans. Av = 2.41, Ri = 0.485 kΩ)


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers