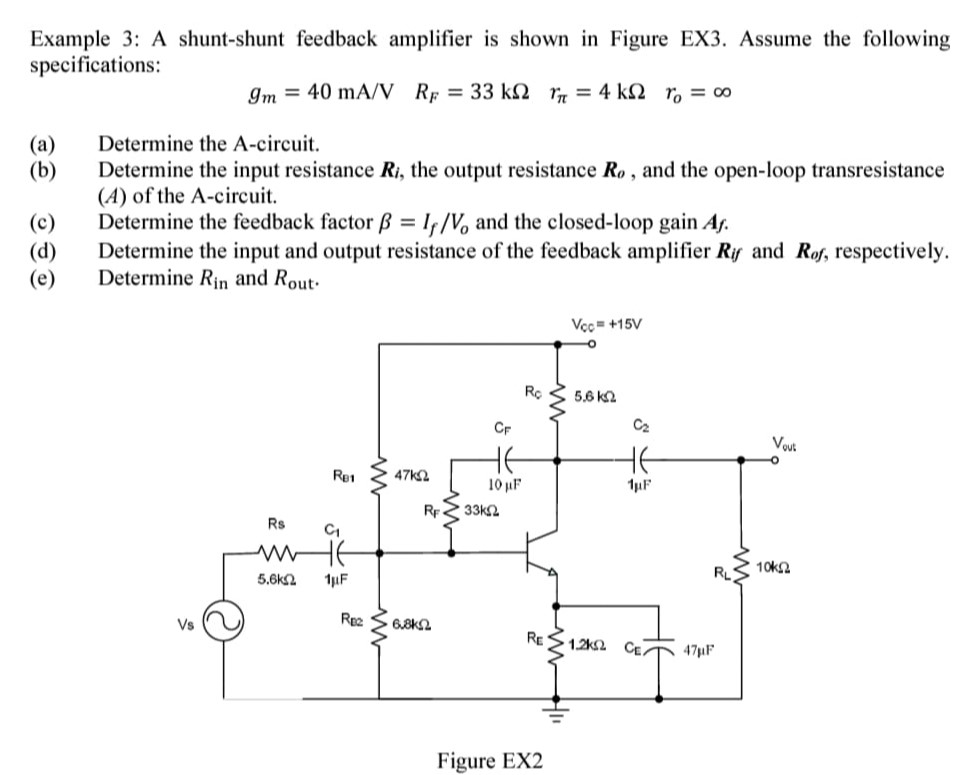
Example 3: A shunt-shunt feedback amplifier is shown in Figure EX3. Assume the following specifications: gm = 40 mA/V RF = 33 kΩ rπ = 4 kΩ ro = ∞ (a) Determine the A-circuit. (b) Determine the input resistance Ri, the output resistance Ro, and the open-loop transresistance (A) of the A-circuit. (c) Determine the feedback factor β = If/Vo and the closed-loop gain Af. (d) Determine the input and output resistance of the feedback amplifier Rif and Rof, respectively. (e) Determine Rin and Rout . Figure EX2