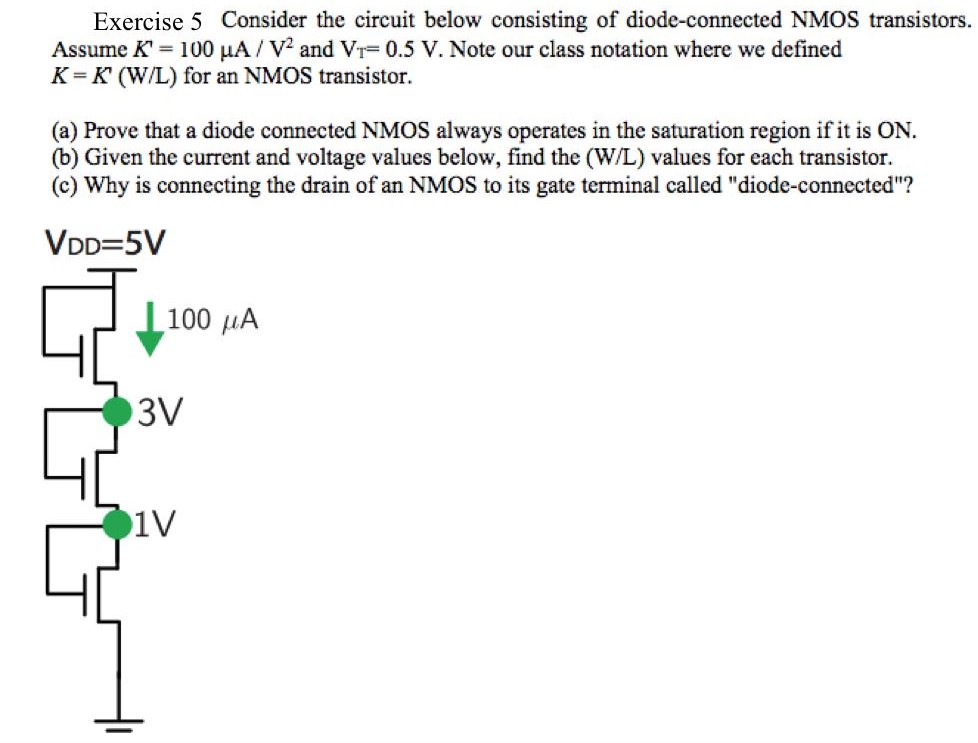
Exercise 5 Consider the circuit below consisting of diode-connected NMOS transistors. Assume K′ = 100 μA/V2 and VT = 0.5 V. Note our class notation where we defined K = K′(W/L) for an NMOS transistor. (a) Prove that a diode connected NMOS always operates in the saturation region if it is ON. (b) Given the current and voltage values below, find the (W/L) values for each transistor. (c) Why is connecting the drain of an NMOS to its gate terminal called "diode-connected"?