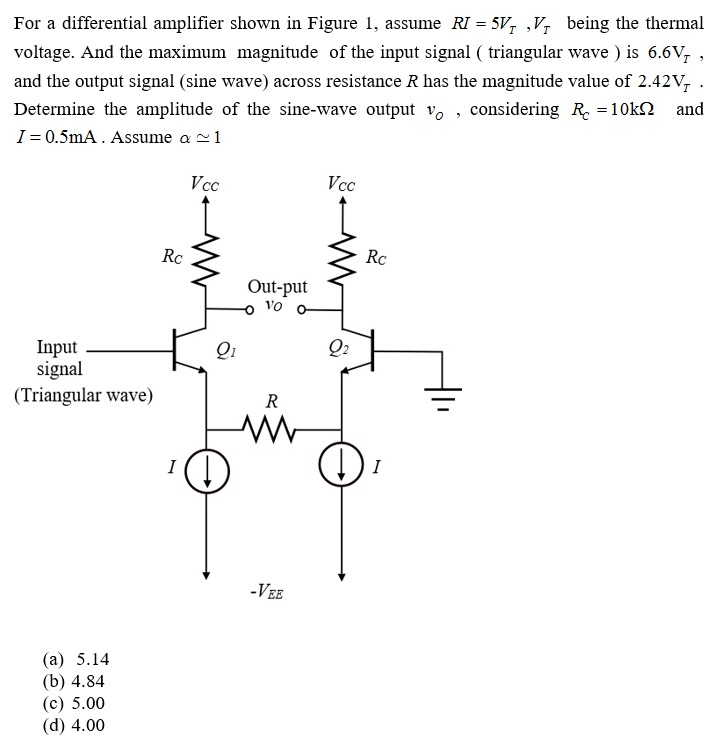
For a differential amplifier shown in Figure 1, assume RI = 5 VT, VT being the thermal voltage. And the maximum magnitude of the input signal ( triangular wave ) is 6.6VT, and the output signal (sine wave) across resistance R has the magnitude value of 2.42VT. Determine the amplitude of the sine-wave output vo, considering RC = 10 kΩ and I = 0.5 mA. Assume α≃1 (a) 5.14 (b) 4.84 (c) 5.00 (d) 4.00