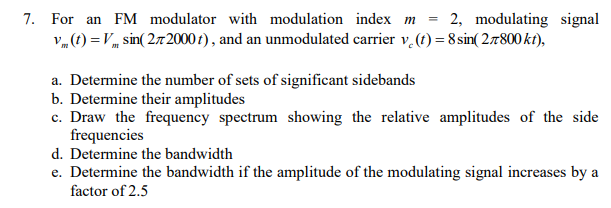
For an FM modulator with modulation index m = 2, modulating signal vm(t) = Vmsin(2π2000t), and an unmodulated carrier vc(t) = 8 sin(2π800 kt), a. Determine the number of sets of significant sidebands b. Determine their amplitudes c. Draw the frequency spectrum showing the relative amplitudes of the side frequencies d. Determine the bandwidth e. Determine the bandwidth if the amplitude of the modulating signal increases by a factor of 2.5