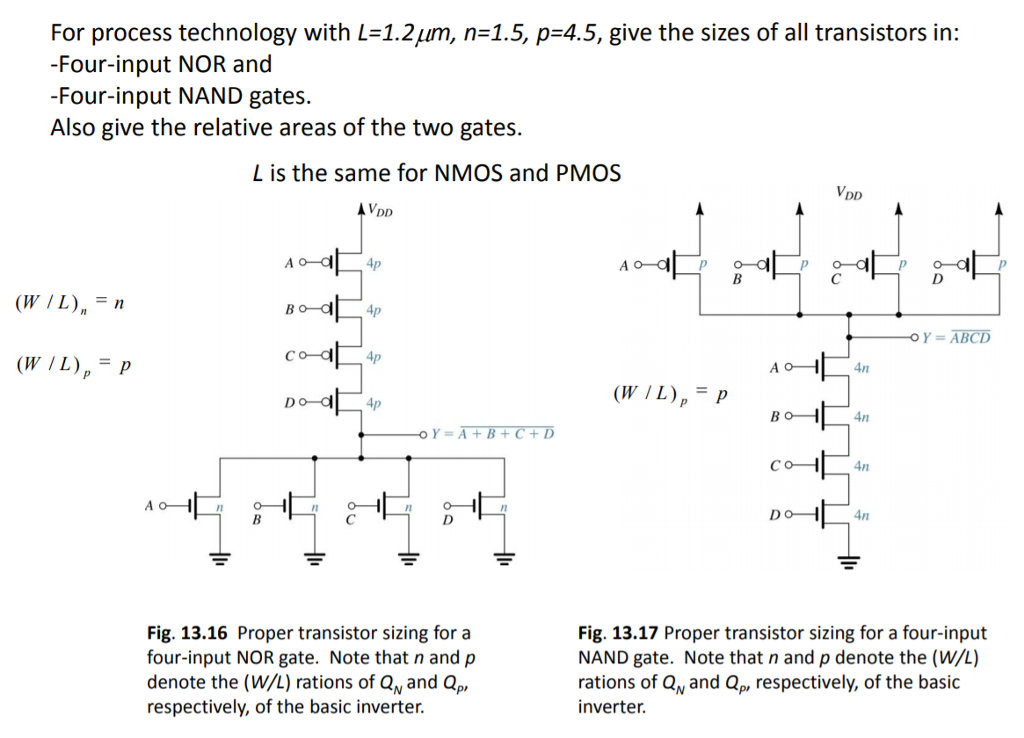
For process technology with L = 1.2 um, n = 1.5, p = 4.5, give the sizes of all transistors in: -Four-input NOR and -Four-input NAND gates. Also give the relative areas of the two gates. is the same for NMOS and PMOS Fig. 13.16 Proper transistor sizing for a four-input NOR gate. Note that n and p denote the (W/L) rations of QN and QP, respectively, of the basic inverter. Fig. 13.17 Proper transistor sizing for a four-input NAND gate. Note that n and p denote the (W/L) rations of QN and QP, respectively, of the basic inverter.


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers