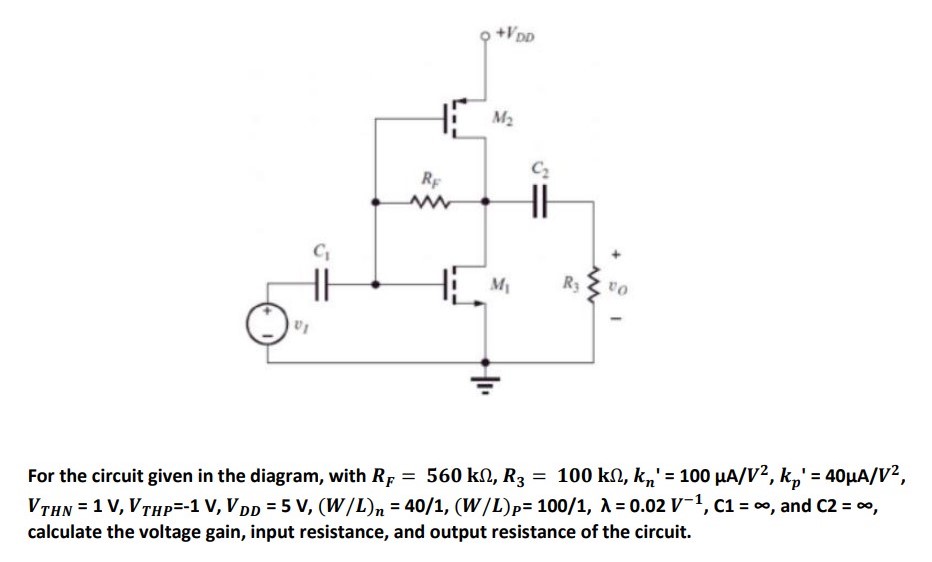
For the circuit given in the diagram, with RF = 560 kΩ, R3 = 100 kΩ, kn′ = 100 μA/V2, kp′ = 40 μA/V2, VTHN = 1 V, VTHP = −1 V, VDD = 5 V, (W/L)n = 40/1, (W/L)P = 100/1, λ = 0.02 V−1, C1 = ∞, and C2 = ∞, calculate the voltage gain, input resistance, and output resistance of the circuit.