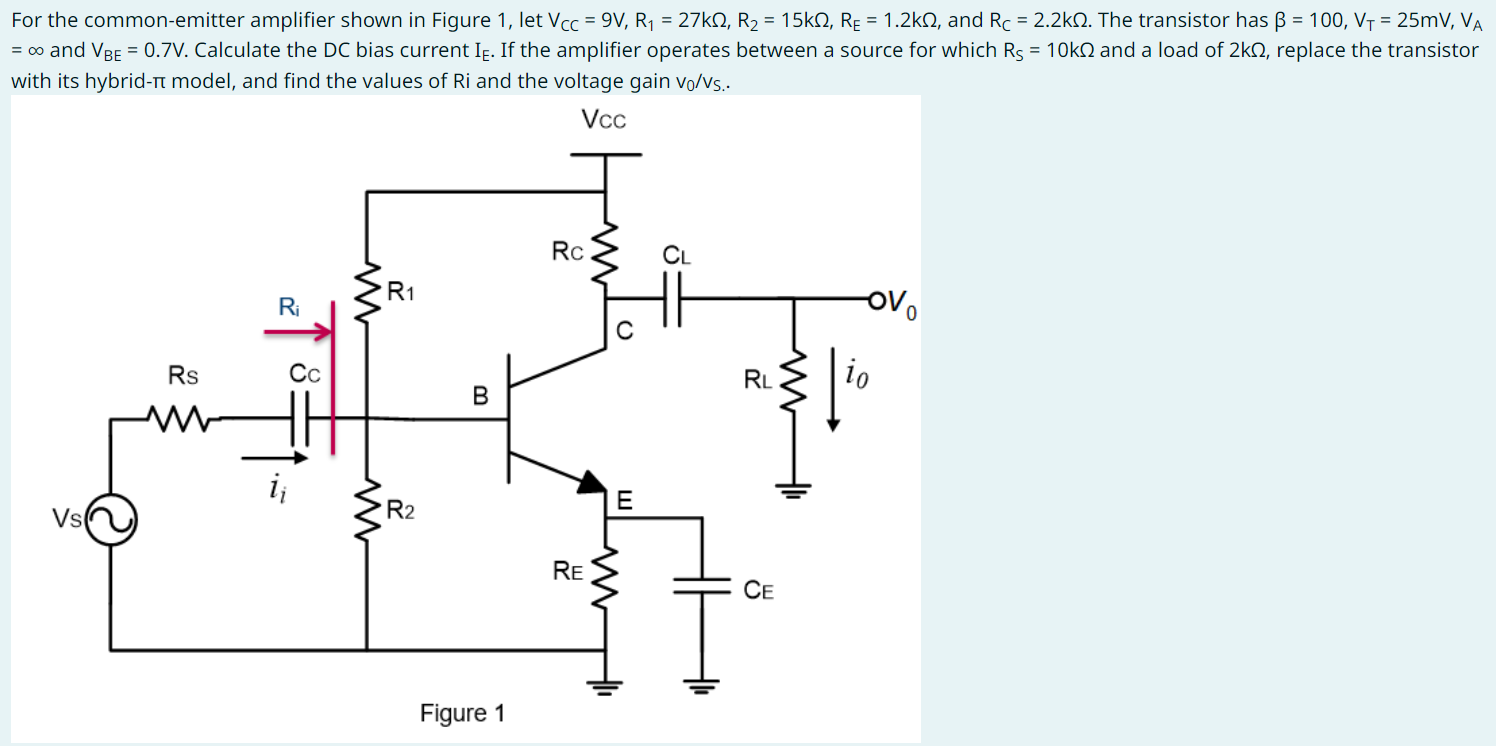
For the common-emitter amplifier shown in Figure 1 , let VCC = 9 V, R1 = 27 kΩ, R2 = 15 kΩ, RE = 1.2 kΩ, and RC = 2.2 kΩ. The transistor has β = 100, VT = 25 mV, VA = ∞ and VBE = 0.7 V. Calculate the DC bias current IE. If the amplifier operates between a source for which RS = 10 kΩ and a load of 2 kΩ, replace the transistor with its hybrid- π model, and find the values of Ri and the voltage gain v0/vs. Figure 1