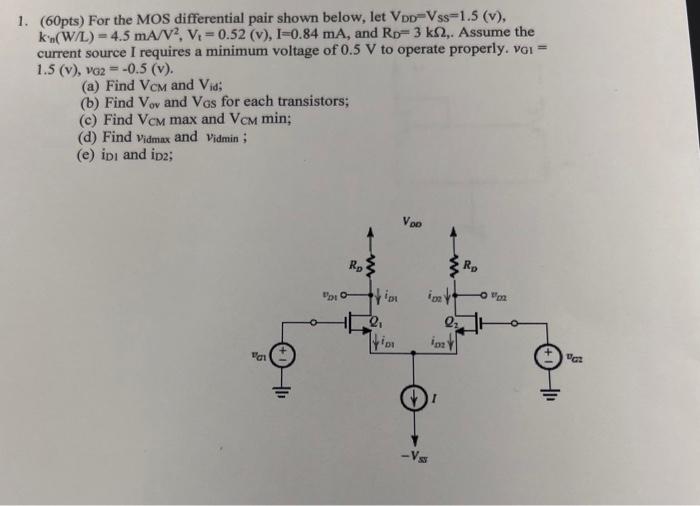
For the MOS differential pair shown below, let VDD = VSS = 1.5 (v), k’n(W/L) = 4.5 mA/V2, Vt = 0.52 (v), I = 0.84 mA, and RD = 3 kΩ, Assume the current source I requires a minimum voltage of 0.5 V to operate properly, vG1 = 1.5(v), vG2 = −0.5(v). (a) Find VCM and Vid; (b) Find Vov and VGS for each transistors; (c) Find VCMmax and VCM min; (d) Find vidmax and vidmin ; (e) iD1 and iD2;


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers