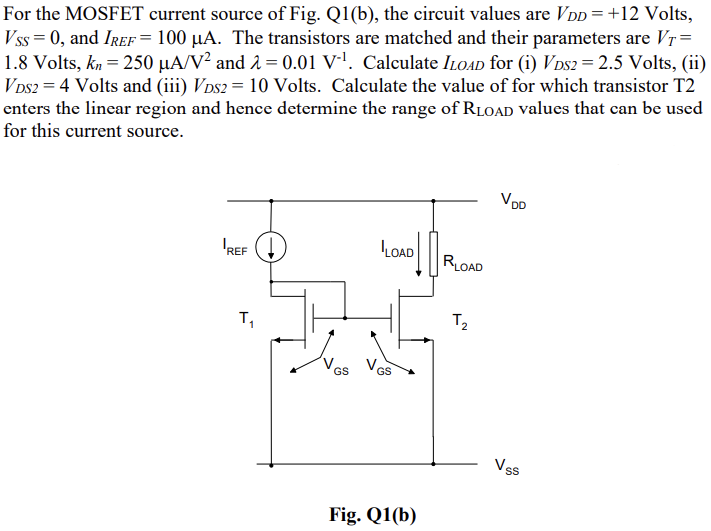
For the MOSFET current source of Fig. Q1(b), the circuit values are VDD = +12 Volts, VSS = 0, and IREF = 100 μA. The transistors are matched and their parameters are VT = 1.8 Volts, kn = 250 μA/V2 and λ = 0.01 V−1. Calculate ILOAD for (i) VDS2 = 2.5 Volts, (ii) VDS2 = 4 Volts and (iii) VDS2 = 10 Volts. Calculate the value of for which transistor T2 enters the linear region and hence determine the range of RLOAD values that can be used for this current source. Fig. Q1(b)