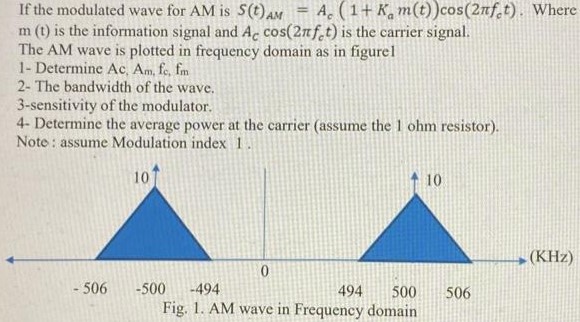
If the modulated wave for AM is S(t)AM = Ac(1 + Kam(t))cos(2πfct). Where m(t) is the information signal and Accos(2πfct) is the carrier signal. The AM wave is plotted in frequency domain as in figure1- Determine Ac, Am, fc, fm 2- The bandwidth of the wave. 3 -sensitivity of the modulator. 4- Determine the average power at the carrier (assume the 1 ohm resistor). Noto : assume Modulation index 1. Fig. 1. AM wave in Frequency domain