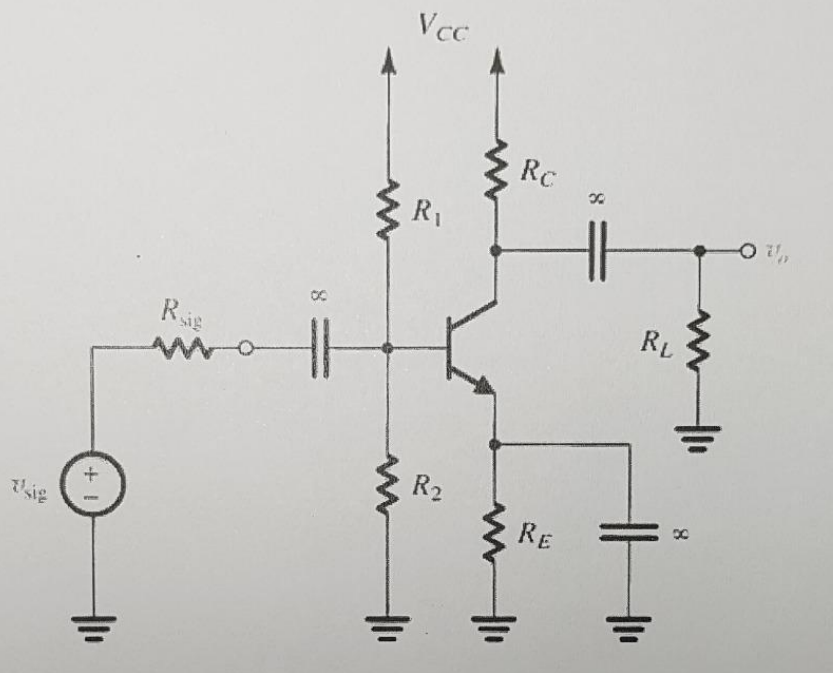
In the circuit diagram, given the BJT parameters: β = 100, VA = −50 V, VCC = 5.7 V, Rsig = 2 kΩ, R1 = 30 kΩ, R2 = 15 kΩ, RC = 1 kΩ, RE = 1.1 kΩ, RL = 4 kΩ, calculate the following. (18 points) (a) The operating point of the BJT IBQ, ICQ, VCEQ (6 points) (b) Draw the small-signal equivalent circuit of the circuit. (4 points) (c) Calculate the input resistance (Rin), output resistance (Rout ), voltage gain (Av), and overall voltage gain (Gv). (8 points)