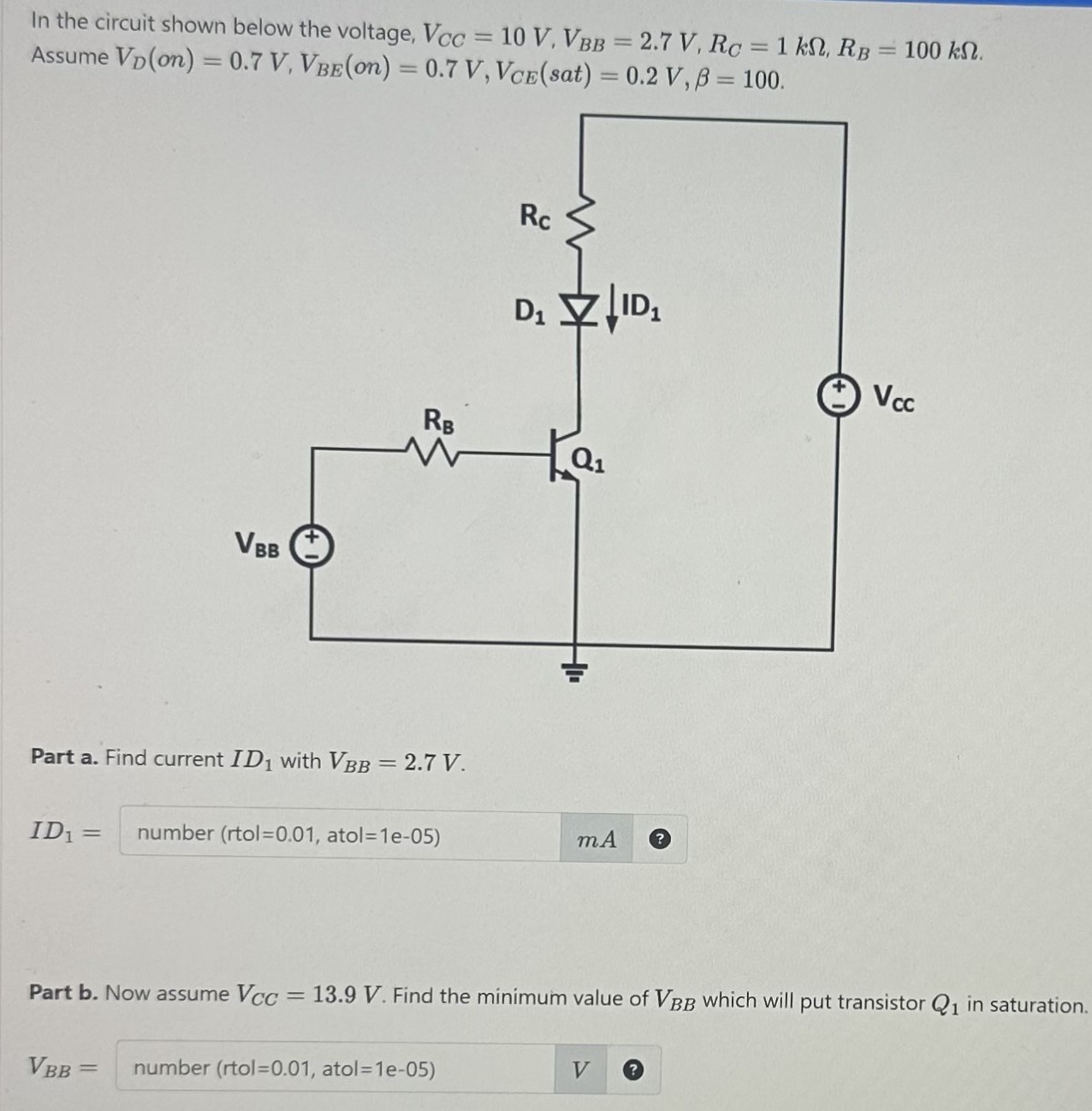
In the circuit shown below the voltage, VCC = 10 V, VBB = 2.7 V, RC = 1 kΩ, RB = 100 kΩ. Assume VD(on) = 0.7 V, VBE(on) = 0.7 V, VCE(sat) = 0.2 V, β = 100. Part a. Find current ID1 with VBB = 2.7 V. ID1 = number mA Part b. Now assume VCC = 13.9 V. Find the minimum value of VBB which will put transistor Q1 in saturation. VBB = number (rtol = 0.01, atol = 1 e−05) V