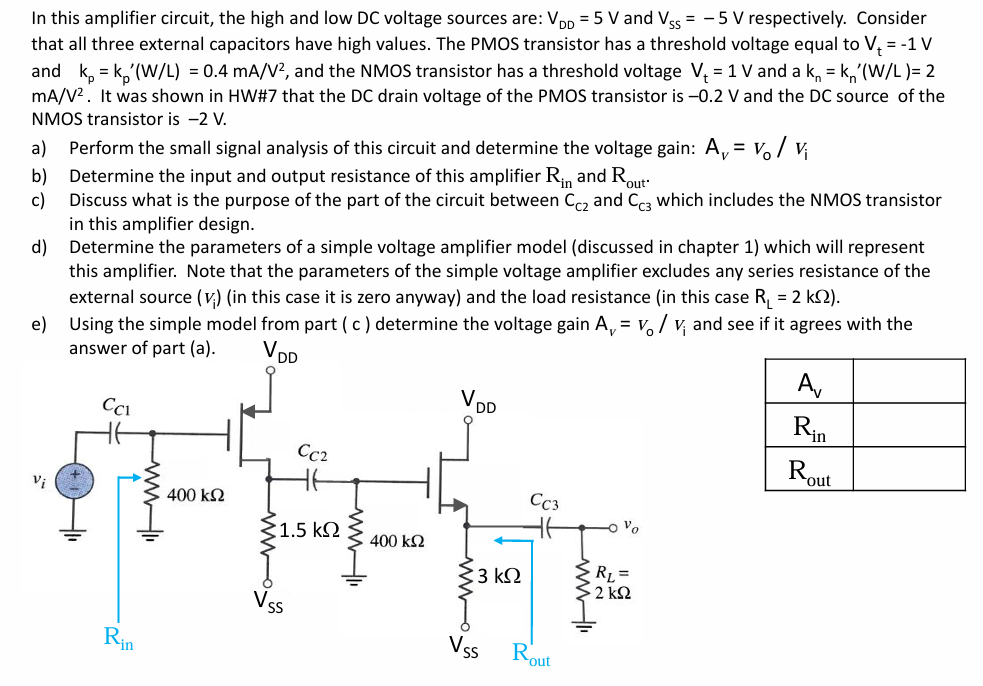
In this amplifier circuit, the high and low DC voltage sources are: VDD = 5 V and VSS = −5 V respectively. Consider that all three external capacitors have high values. The PMOS transistor has a threshold voltage equal to Vt = −1 V and kp = kp′(W/L) = 0.4 mA/V2, and the NMOS transistor has a threshold voltage Vt = 1 V and a kn = kn′(W/L) = 2 mA/V2. It was shown in HW#7 that the DC drain voltage of the PMOS transistor is −0.2 V and the DC source of the NMOS transistor is −2 V. a) Perform the small signal analysis of this circuit and determine the voltage gain: AV = Vo/Vi b) Determine the input and output resistance of this amplifier Rin and Rout . c) Discuss what is the purpose of the part of the circuit between CC2 and CC3 which includes the NMOS transistor in this amplifier design. d) Determine the parameters of a simple voltage amplifier model (discussed in chapter 1) which will represent this amplifier. Note that the parameters of the simple voltage amplifier excludes any series resistance of the external source ( Vi ) (in this case it is zero anyway) and the load resistance (in this case RL = 2 kΩ ). e) Using the simple model from part (c) determine the voltage gain AV = Vo/Vi and see if it agrees with the answer of part (a). VDD