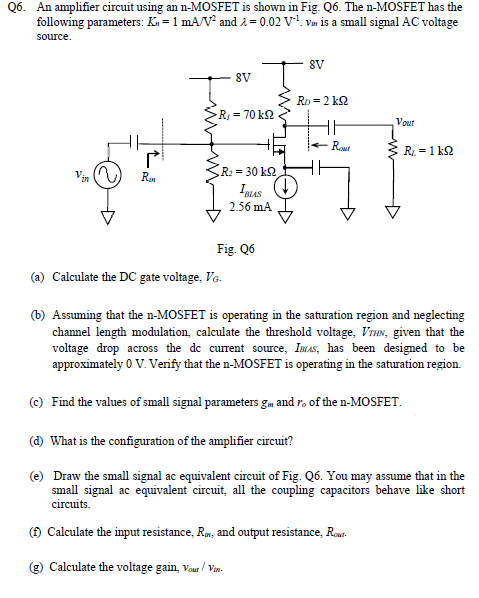
Q6. An amplifier circuit using an n-MOSFET is shown in Fig. Q6. The n-MOSFET has the following parameters: Kn = 1 mA/V2 and λ = 0.02 V−1. vin is a small signal AC voltage source. Fig. Q6 (a) Calculate the DC gate voltage, VG. (b) Assuming that the n-MOSFET is operating in the saturation region and neglecting channel length modulation, calculate the threshold voltage, VTHN, given that the voltage drop across the dc current source, IBUS, has been designed to be approximately 0 V. Verify that the n-MOSFET is operating in the saturation region. (c) Find the values of small signal parameters gm and ro of the n-MOSFET. (d) What is the configuration of the amplifier circuit? (e) Draw the small signal ac equivalent circuit of Fig. Q6. You may assume that in the small signal ac equivalent circuit, all the coupling capacitors behave like short circuits. (f) Calculate the input resistance, Rin, and output resistance, Rout . (g) Calculate the voltage gain, vout/vin.