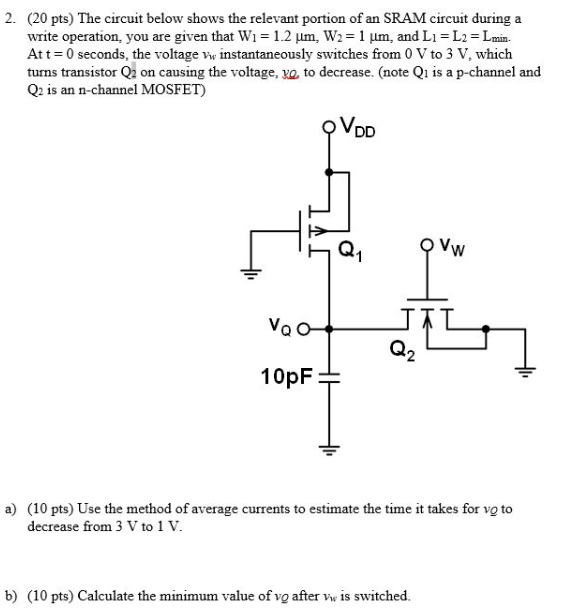
The circuit below shows the relevant portion of an SRAM circuit during a write operation, you are given that W1 = 1.2 μm, W2 = 1 μm, and L1 = L2 = Lmin. At t = 0 seconds, the voltage vw instantaneously switches from 0 V to 3 V, which turns transistor Q2 on causing the voltage, vQ, to decrease. (note Q1 is a p-channel and Q2 is an n-channel MOSFET) a) (10 pts) Use the method of average currents to estimate the time it takes for vQ to decrease from 3 V to 1 V. b) (10 pts) Calculate the minimum value of vQ after vw is switched.