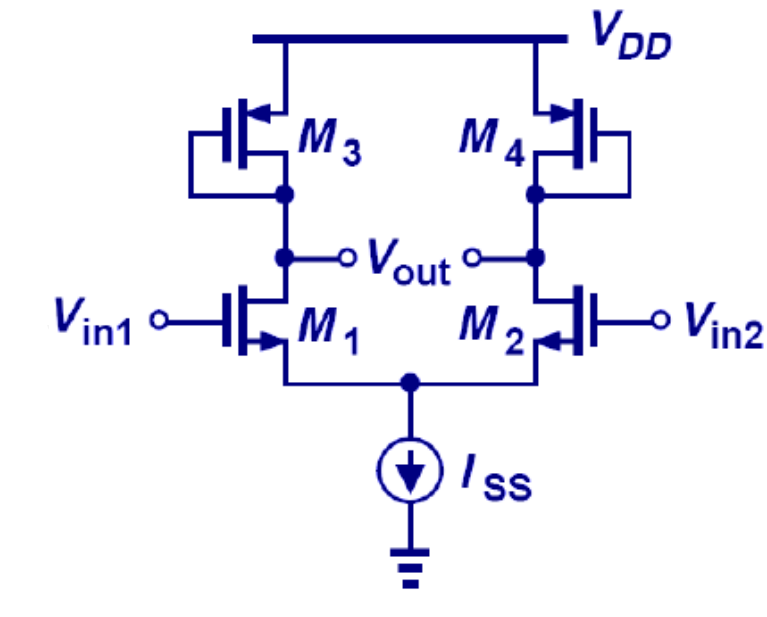
The circuit shown above is a MOS differential amplifier with the drain resistors RD implemented using diode-connected PMOS transistors, M3 and M4. Let M1 and M2 be matched, and M3 and M4 be matched. If λ>0 and gm ro >> 1: (a) Use circuit splitting technique to derive an expression for the differential voltage gain (Ad) (b) Determine the common-mode gain (A_CM) assuming that the tail current source (Iss) is non-ideal so that it has a finite output resistance Rss (parallel with the tail current source)
The circuit shown above is a MOS differential amplifier with the drain resistors RD implemented using diode-connected PMOS transistors, M3 and M4. Let M1 and M2 be matched, and M3 and M4 be matched. If λ>0 and gm ro >> 1:
(a) Use circuit splitting technique to derive an expression for the differential voltage gain (Ad)
(b) Determine the common-mode gain (ACM) assuming that the tail current source (Iss) is non-ideal so that it has a finite output resistance Rss (parallel with the tail current source)


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers