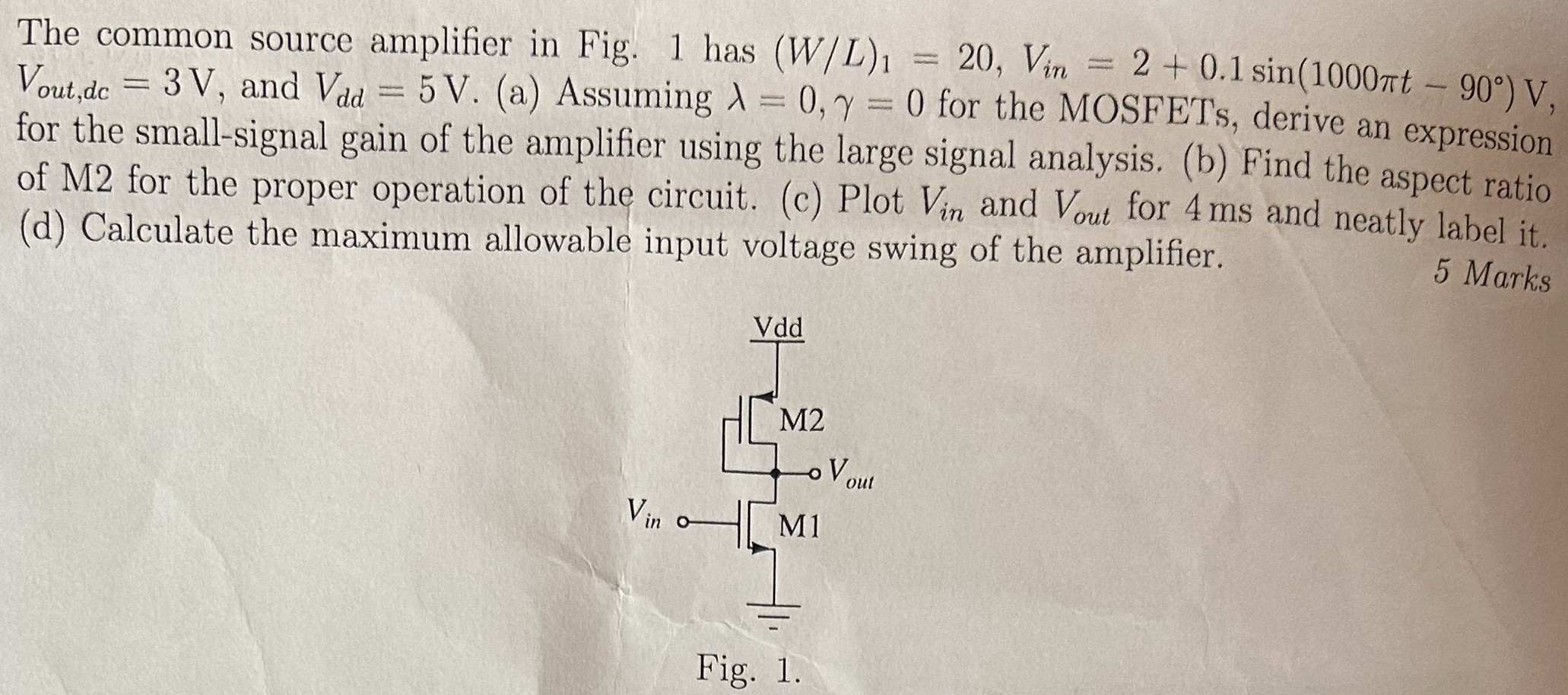
The common source amplifier in Fig. 1 has (W/L)1 = 20, Vin = 2 + 0.1sin(1000πt − 90∘) V, Vout , dc = 3 V, and Vdd = 5 V. (a) Assuming λ = 0, γ = 0 for the MOSFETs, derive an expression for the small-signal gain of the amplifier using the large signal analysis. (b) Find the aspect ratio of M2 for the proper operation of the circuit. (c) Plot Vin and Vout for 4 ms and neatly label it. (d) Calculate the maximum allowable input voltage swing of the amplifier. 5 Marks Fig. 1.