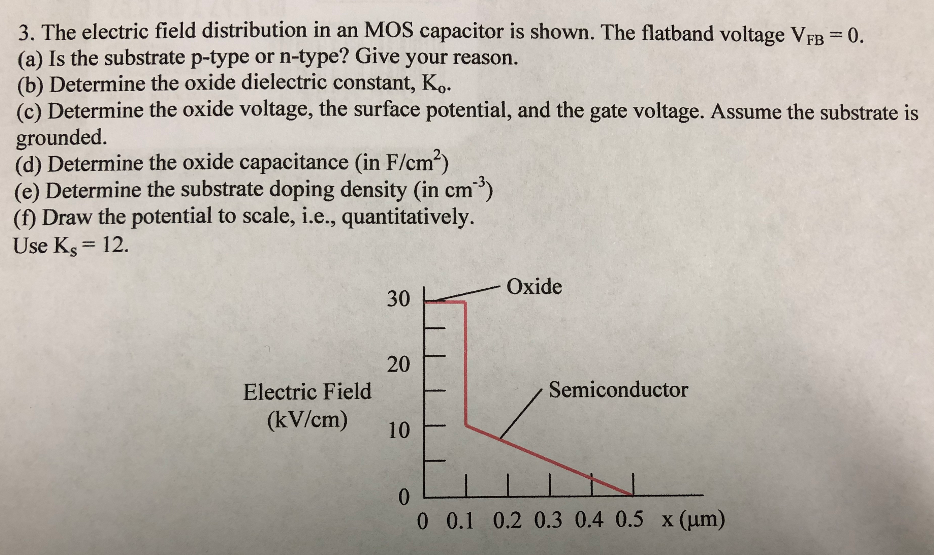
The electric field distribution in an MOS capacitor is shown. The flatband voltage VFB = 0. (a) Is the substrate p-type or n-type? Give your reason. (b) Determine the oxide dielectric constant, Ko. (c) Determine the oxide voltage, the surface potential, and the gate voltage. Assume the substrate is grounded. (d) Determine the oxide capacitance (in F/cm2) (e) Determine the substrate doping density (in cm−3) (f) Draw the potential to scale, i.e. , quantitatively. Use Ks = 12.