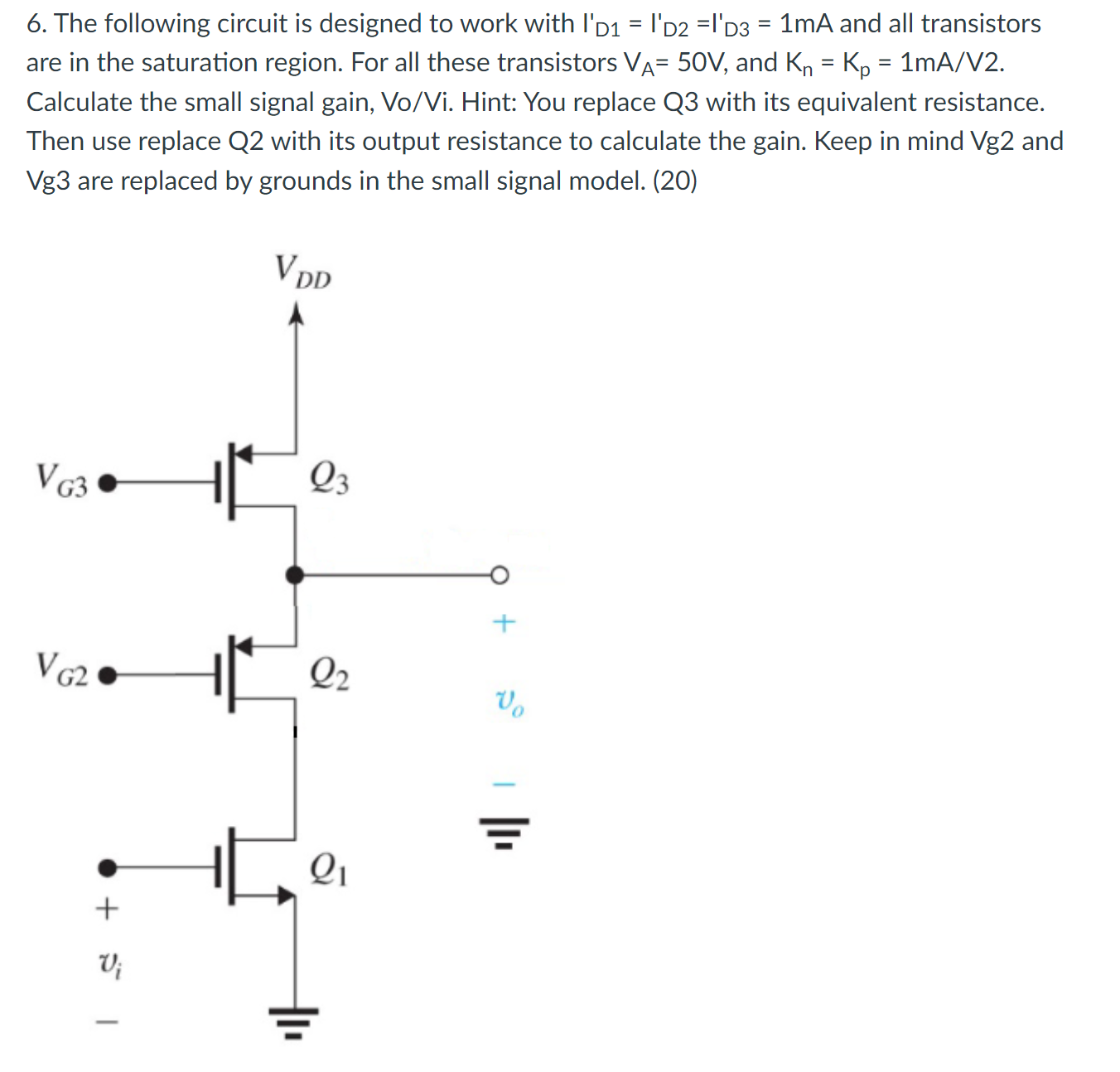
The following circuit is designed to work with ID1' = ID2' = ID3' = 1 mA and all transistors are in the saturation region. For all these transistors VA = 50 V, and Kn = Kp = 1 mA/V2. Calculate the small signal gain, Vo/Vi. Hint: You replace Q3 with its equivalent resistance. Then use replace Q2 with its output resistance to calculate the gain. Keep in mind Vg2 and Vg3 are replaced by grounds in the small signal model. (20)