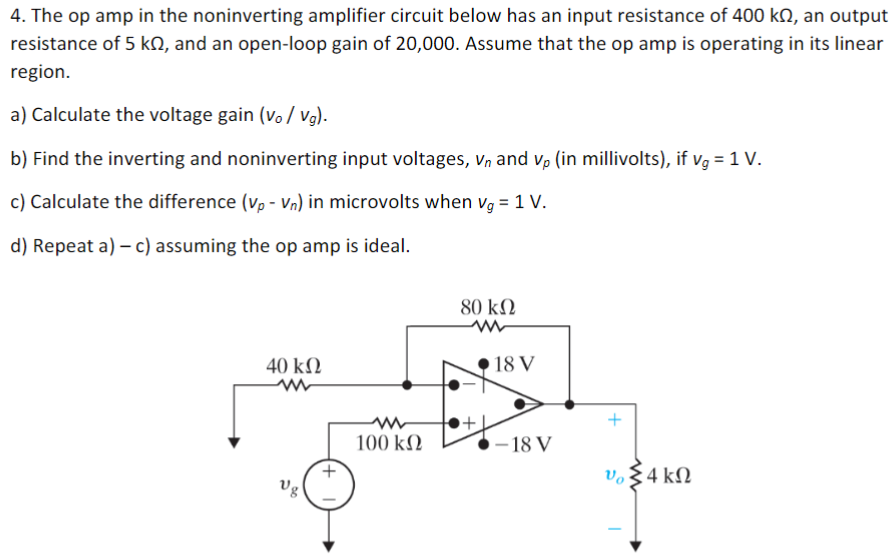
The op amp in the noninverting amplifier circuit below has an input resistance of 400 kΩ, an output resistance of 5 kΩ, and an open-loop gain of 20,000 . Assume that the op amp is operating in its linear region. a) Calculate the voltage gain (vo/vg). b) Find the inverting and noninverting input voltages, vn and vp (in millivolts), if vg = 1 V. c) Calculate the difference (vp − vn) in microvolts when vg = 1 V. d) Repeat a) - c) assuming the op amp is ideal.