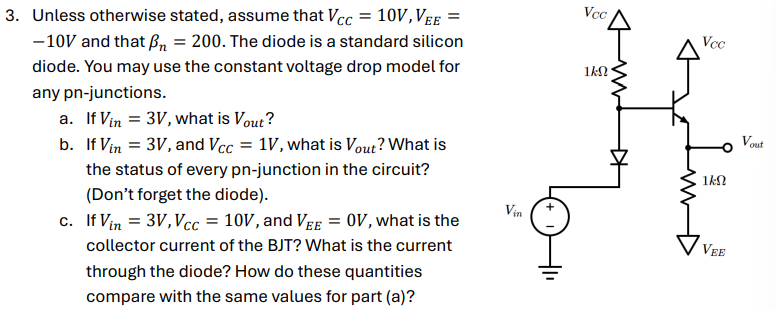
Unless otherwise stated, assume that VCC = 10 V, VEE = -10 V and that βn = 200. The diode is a standard silicon diode. You may use the constant voltage drop model for any pn-junctions. a. If Vin = 3 V, what is Vout? b. If Vin = 3 V, and VCC = 1 V, what is Vout? What is the status of every pn-junction in the circuit? (Don't forget the diode). c. If Vin = 3 V, VCC = 10 V, and VEE = 0 V, what is the collector current of the BJT? What is the current through the diode? How do these quantities compare with the same values for part (a)?


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers