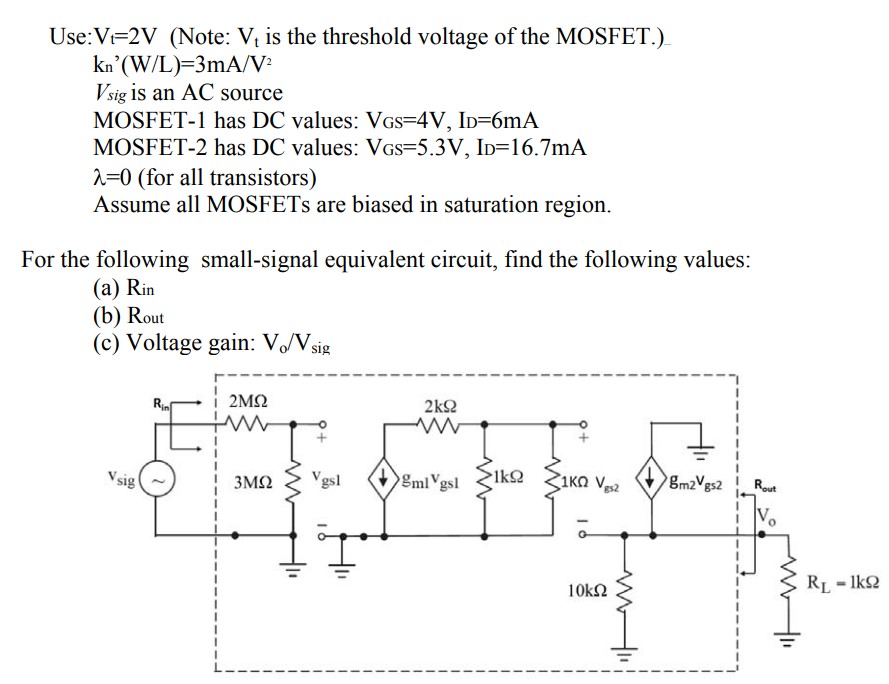
Use: Vt = 2 V (Note: Vt is the threshold voltage of the MOSFET.) kn’(W/L) = 3 mA/V2 Vsig is an AC source MOSFET-1 has DC values: VGS = 4 V,ID = 6 mA MOSFET-2 has DC values: VGS = 5.3 V, ID = 16.7 mA λ = 0 (for all transistors) Assume all MOSFETs are biased in saturation region. For the following small-signal equivalent circuit, find the following values: (a) Rin (b) Rout (c) Voltage gain: Vo/Vsig


You'll get a detailed, step-by-step and expert verified solution.
 Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers
Work With Experts to Reach at Correct Answers