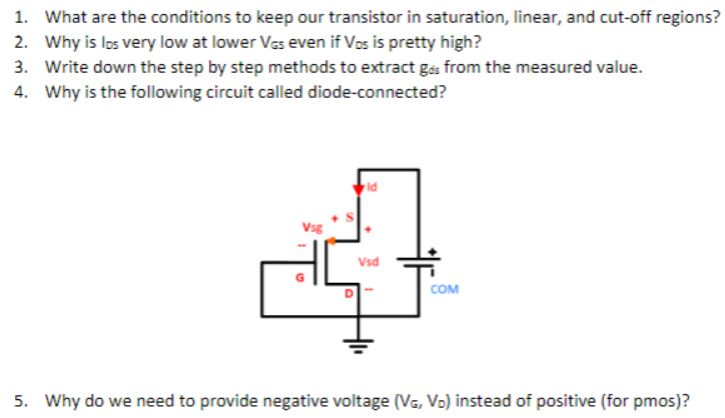
What are the conditions to keep our transistor in saturation, linear, and cut-off regions? Why is los very low at lower VGS even if VDS is pretty high? Write down the step by step methods to extract gds from the measured value. Why is the following circuit called diode-connected? Why do we need to provide negative voltage (VG, VD) instead of positive (for pmos)?