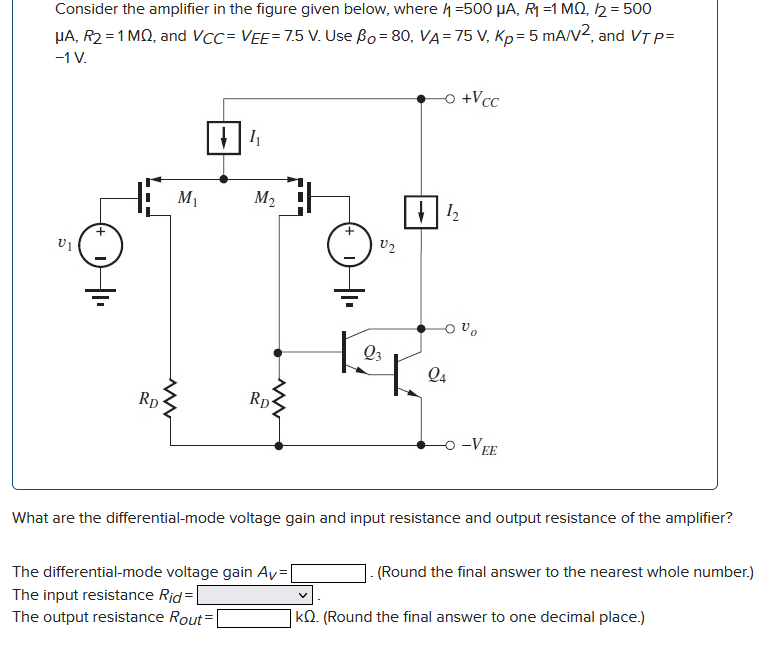
What are the differential-mode voltage gain and input resistance and output resistance of the amplifier? The differential-mode voltage gain AV = . (Round the final answer to the nearest whole number.) The input resistance Rid = The output resistance ROut = kΩ. (Round the final answer to one decimal place.) Consider the amplifier in the figure given below, where I1 = 500 μA, R1 = 1 MΩ, I2 = 500 μA, R2 = 1 MΩ, and VCC = VEE = 7.5 V. Use βO = 80, VA = 75 V, Kp = 5 mA/V2, and VTP = −1 V.