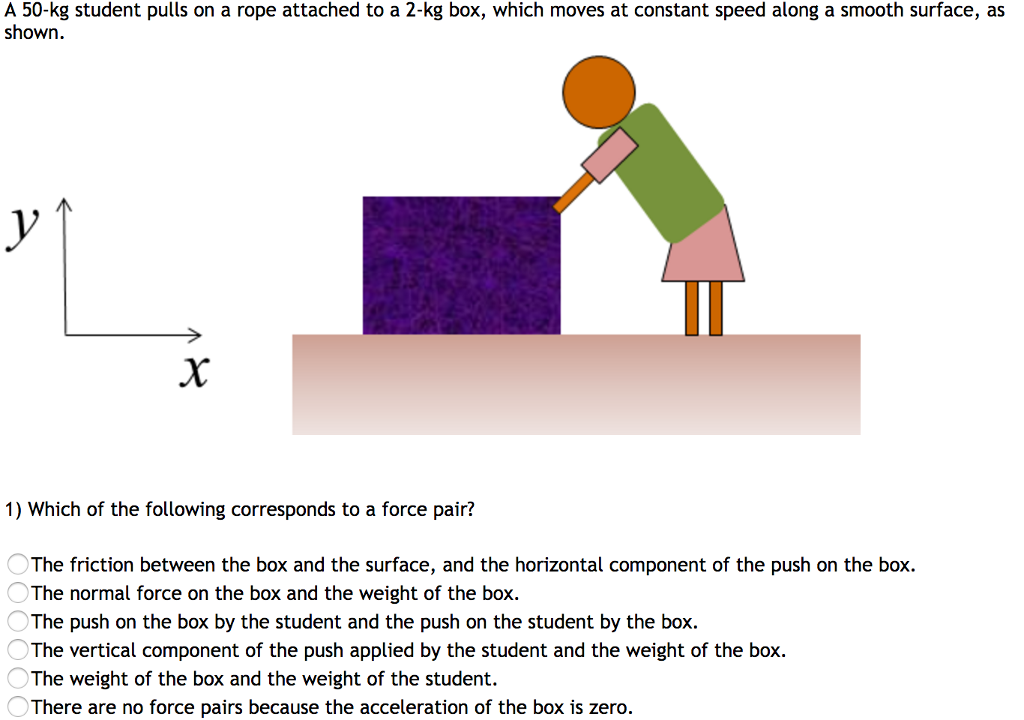
A 50-kg student pulls on a rope attached to a 2-kg box, which moves at constant speed along a smooth surface, as shown. Which of the following corresponds to a force pair? The friction between the box and the surface, and the horizontal component of the push on the box. The normal force on the box and the weight of the box. The push on the box by the student and the push on the student by the box. The vertical component of the push applied by the student and the weight of the box. The weight of the box and the weight of the student. There are no force pairs because the acceleration of the box is zero.