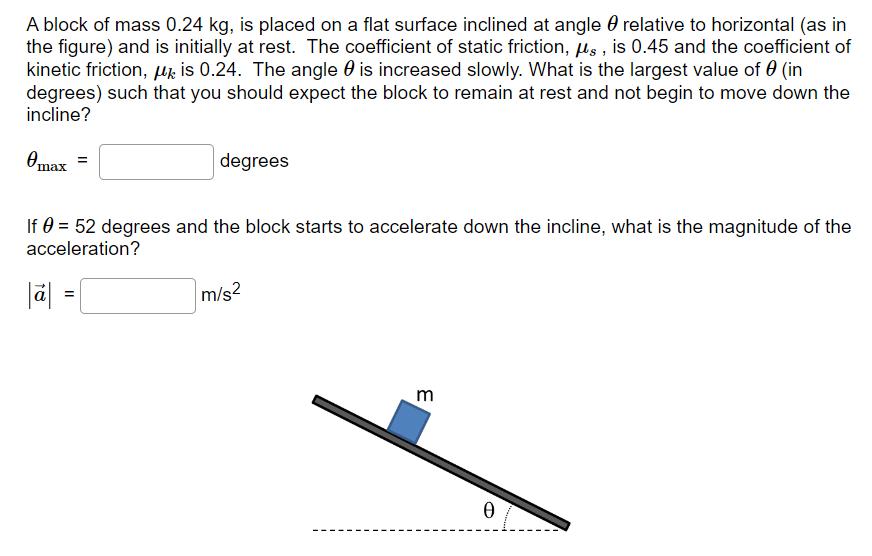
A block of mass 0.24 kg, is placed on a flat surface inclined at angle θ relative to horizontal (as in the figure) and is initially at rest. The coefficient of static friction, μs, is 0.45 and the coefficient of kinetic friction, μk is 0.24. The angle θ is increased slowly. What is the largest value of θ (in degrees) such that you should expect the block to remain at rest and not begin to move down the incline? θmax = degrees If θ = 52 degrees and the block starts to accelerate down the incline, what is the magnitude of the acceleration? |a→| = m/s2